Figure 3. Biochemical evaluation of the interaction of CRBP1 with abn-CBD.
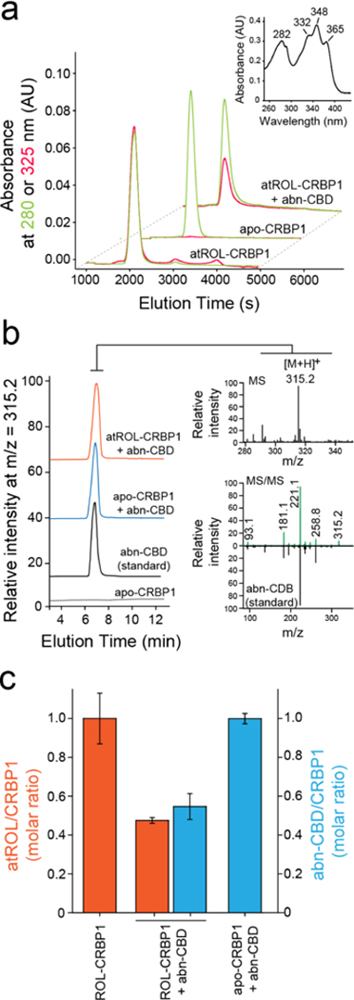
(a) Incubation of vitamin A-bound CRBP1 with abn-CBD led to depletion of atROL as evident by decreased absorption at 325 nm (red trace) in relation to the protein absorbance at 280 nm (green trace) in the repurified sample. (inset) UV/vis absorbance spectrum of atROL-bound CRBP1. (b) MS-based detection of abn-CBD in the CRBP1 fractions. The extracts of the protein samples preincubated abn-CBD and repurified revealed presence of intense ion peak at m/z = 315.2 [M + H]+. The molecular identification of this parent ion as corresponding to abn-CBD was achieved by comparing the MS/MS fragmentation pattern with a synthetic standard of the ligand. (c) Quantification of the ligand/protein ratios after incubation of vitamin A-bound CRBP1 with 2 molar excess of abn-CBD. The degree of atROL elimination from the protein is proportional to the amount of abn-CBD bound suggesting that these two ligands compete for the same binding site.
