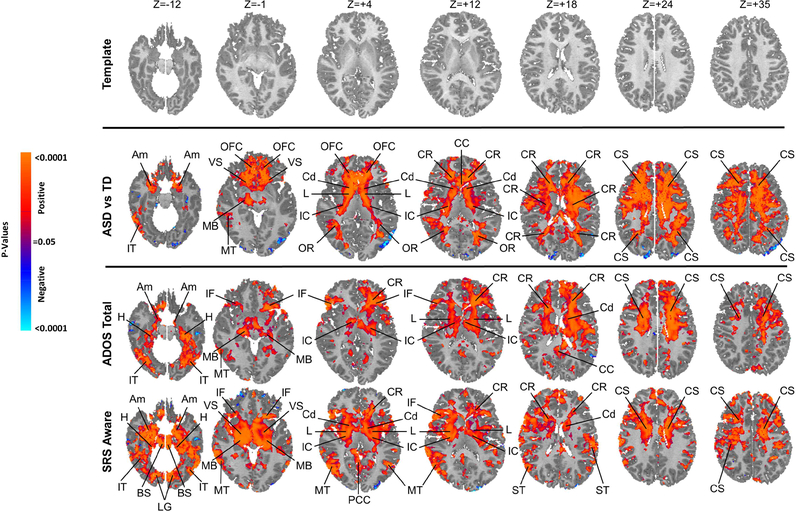
Figure 1. Group Comparisons and Symptom Correlations.
The right sides of the images correspond to the right side of the brain. All analyses control for the effects of age and sex, and the significance levels in all maps are FDR-corrected for the number of statistical comparisons.First Row Shown is the T1-weighted anatomical template to which rCBF values for all participants were mapped at transaxial slice levels positioned parallel to the Anterior Commissure-Posterior Commissure (AC-PC) line, and corresponding to the positioning of the statistical maps shown in the other rows. The z-values represent slice level (in millimeters) in the Talairach coordinate system.
Second Row This shows the statistically significant differences in rCBF values between the ASD group and TD controls while covarying for age and sex, displayed at a threshold of P<0.05 after correction for multiple comparisons. Voxels in red indicate significantly increased rCBF, and blue voxels reduced rCBF, in ASD relative to controls. Perfusion values at rest in the ASD group were higher bilaterally throughout white matter of all the frontal lobe, internal capsule, and dorsal parietal lobe, and in gray matter of the basal ganglia, thalamus, and amygdala.
Third & Fourth Rows Red and blue voxels represent, respectively, significant positive or inverse correlations of ADOS total scores and SRS social affect scores with rCBF values in the ASD group, after FDR correction for multiple comparisons.
Abbreviations Am: amygdala; BS: brainstem; CC: corpus callosum; Cd: caudate; CR: corona radiata; CS: centrum semovale; H: hippocampus; IC: internal capsule; IF: inferior frontal gyrus; IT: inferior temporal gyrus; L: lenticular nucleus; MB: midbrain; MT: middle temporal gyrus; OFC: orbitofrontal cortex; OR optic radiations; PCC: posterior cingulate cortex; ST: superior temporal gyrus; Th: thalamus; VS: ventral striatum