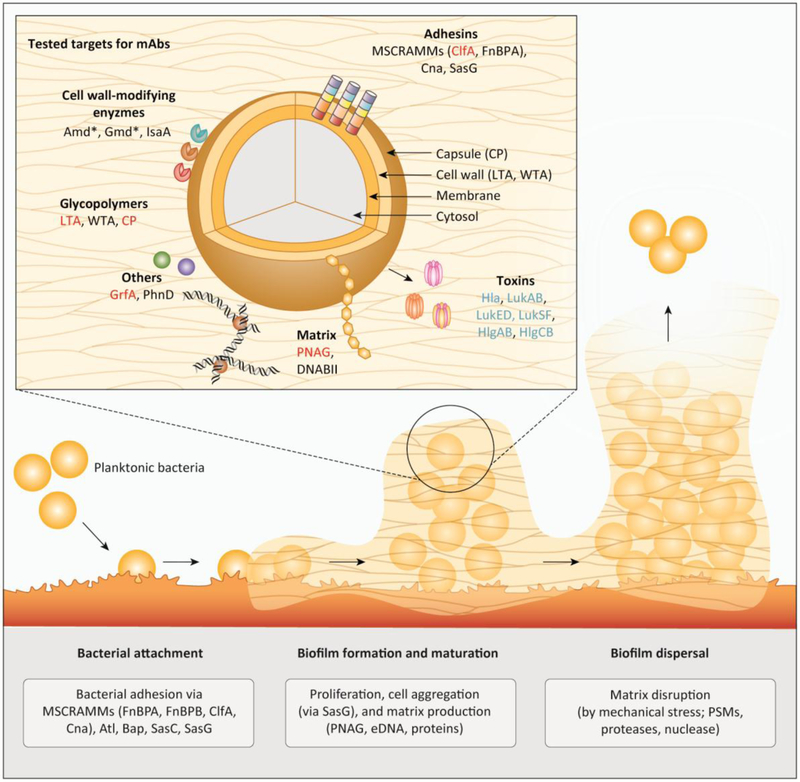
Figure 1: Overview on tested targets for an antibody-based preventive or therapeutic strategy against biofilm-associated S. aureus infections.
Main figure: Biofilm formation in staphylococci comprising three main stages: bacterial attachment to a surface, biofilm formation and maturation, and biofilm detachment / dispersal. For the attachment to (a)biotic surfaces, S. aureus relies on a broad spectrum of functionally redundant adhesins such as the MSCRAMMs (ClfA, Cna, FnbA, FnbB). After successful adhesion, bacteria start proliferation and production of the biofilm matrix consisting of eDNA, stabilized by DNABII, PNAG and proteins. Eventually, biofilm dispersal is mediated by mechanical shear stress (e.g. in a blood vessel) or by dispersion factors like PSMs, nuclease, and proteases. Insert: Molecular targets for antibody based therapies tested in preclinical in clinical studies include adhesins and cell-wall modifying enzymes and other cell wall-attached proteins, surface glycopolymers, biofilm matrix components, as well as toxins and immune evasion proteins. Targets from preclinical studies, ongoing clinical trials and failed clinical trials are shown in black, blue and red, respectively. The asterisk indicates that the S. aureus protein autolysin (Atl) is proteolytically processed into two enzymes, autolysin amidase (Amd) and autolysin glucosaminidase (Gmd), which stay non-covalently attached to the cell surface.
Abbreviations: Atl (autolysin); Amd (autolysin amidase); Bap (biofilm-associated protein ); ClfA (clumping factor A); Cna (collagen-binding protein); CP (capsular polysaccharides); DNABII (DNABII family proteins); eDNA (extracellular DNA); FnBPA/FnBPB (fibronectin-binding protein A and B); Gmd (autolysin glucosaminidase); GrfA (ABC transporter); Hla (α-toxin); Hlg (γ-haemolysin); IsaA (Immunodominant staphylococcal antigen A); LTA (lipoteichoic acid); Luk (Leukotoxins); mAb (monoclonal antibody); MSCRAMM (microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecule); PhnD (subunit of alkylphosphonate ABC transporter); PNAG (poly-N-acetyl-ß-(1,6)-glucosamine); PSMs (phenol soluble modulins); Sasc/G (S. aureus surface protein C and G); WTA (wall teichoic acid).