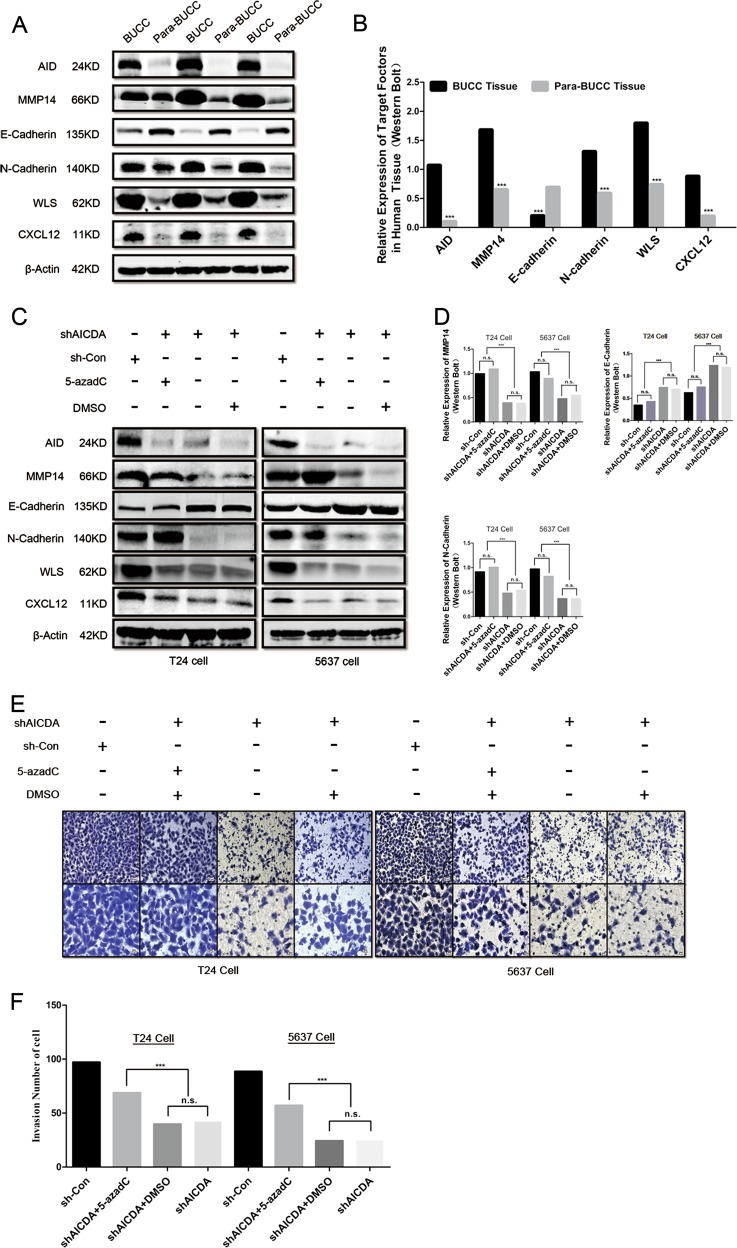
Fig. 5. 5-azadC promotes the expression of MMP14 and upregulates the invasion of T24 and 5637 cells.
a, b Relative expression of AID, MMP14, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, WLS and CXCL12 in the human BUCC and pare-BUCC tissues. As expected, MMP14, CXCL12 and WLS were significantly highly expressed in human BUCC tissues and relatively less expressed in para-BUCC tissues. Furthermore, pro-EMT factor N-cadherin was also upregulated in BUCC tissues, and the relative expression of E-cadherin was down-regulated—the hallmark of EMT. c, d Expression of MMP14 in T24 and 5637 cells was significantly recovered after treated with 5-azadC (P < 0.05), whereas the expression of CXCL12 and WLS remained unchanged. Moreover, the relative expression of N-cadherin and E-cadherin was up- and downregulated, respectively, when treated with 5-azadC. These results indicated that 5-azadC antagonised AID silencing-induced suppression of invasiveness in T24 and 5637 cell. e, f Transwell assay of T24 and 5637 cells. The invasiveness of shAICDA-T24 and shAICDA-5637 cells was recovered with the treatment of 5-azadC (P < 0.05). Original magnification: e, × 200 or × 400, calibration bar at 50 or 25 μm. All the experiments were repeated three times