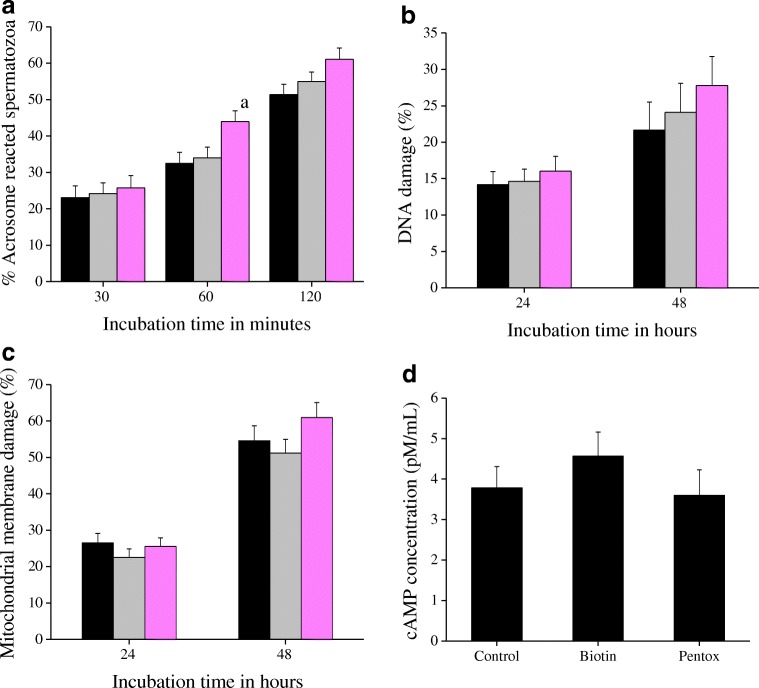
Fig. 1.
a Effect of biotin (10 nM) and PTX (1 mM) on kinetics of acrosome reaction estimated using calcium ionophore (A23187)-induced acrosome reaction assay (CIAR). The swim-up suspension was incubated with ionophore (5 μM) for 30, 60, and 120 min and stained with FITC-PSA for visualization of acrosome sperm head. A total of 500 spermatozoa were assessed for each sample and the data represented as percentage of the difference in the number of ionophore-induced acrosome-reacted spermatozoa to the baseline acrosome-reacted spermatozoa. The results correspond to mean ± SE and the statistical significance value is represented as (a): P < 0.05 vs control. b DNA integrity of the spermatozoa processed with sperm wash medium containing biotin (10 nM) or pentoxifylline (1 mM) at 24 and 48 h after in vitro incubation. The extent of DNA damage in the spermatozoa was assessed by sperm chromatin dispersion (SCD) test. The results correspond to mean ± SE of spermatozoa and the statistical significance value. c Mitochondrial membrane integrity of the spermatozoa processed with sperm wash medium containing biotin (10 nM) or pentoxifylline (1 mM) at 24 and 48 h after in vitro incubation. The spermatozoa were stained with Rhodamine 123 to assess the mitochondrial membrane potential. The results correspond to mean ± SE of percentage of spermatozoa with completely damaged mitochondria. d Effect of biotin (10 nM) and PTX (1 mM) on intracellular cAMP concentration of spermatozoa was measured using cAMP ELISA kit, at 1 h post-swim-up. A total of 15 sets (n = 5 per group) of sample were assessed among the groups and the data is represented as mean ± SE. No statistical significance was found. Black: control; gray: biotin; pink: PTX