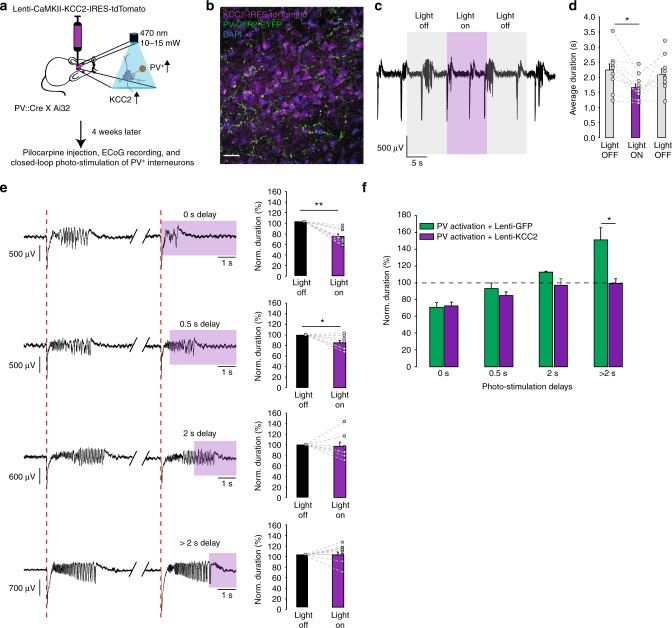
Fig. 5.
KCC2 overexpression in principal neurons prevents the pro-ictal action of PV+ photoactivation during seizures. a Experimental schematic. b Immunofluorescence of the PV-ChR2-EYFP (green), the nuclei staining, DAPI (blue), and the KCC2-IRES-tdTomato (magenta) in an overlaid image. Scale bar 25 µm. c ECoG recordings of ictal discharges before, during and after photoactivation of ChR2-expressing PV+ interneurons in animals that overexpress KCC2 in the cortical principal neurons at the site of pilocarpine injection. d Average duration of ictal discharges during the 10 s baseline (grey) and photostimulation (purple) periods. KCC2 overexpression does not affect the reduction of seizure duration by PV+ photoactivation (c.f. Fig. 2; n = 8 mice, one-way repeated measures ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni correction, *p < 0.05, error bars represent the s.e.m.). e KCC2 overexpression abolishes prolongation of seizures by delayed (>2 s) PV+ photoactivation (n = 10, 7, 7 and 8 mice for the delays of 0, 0.5, 2 and >2 s, paired t-test). Sample traces illustrate pairs of consecutive seizures without and with photostimulation (intervening periods between seizures are omitted; purple rectangles indicate photostimulation). f Normalised duration of ictal discharges by photostimulation of PV+ neurons in mice with (purple) KCC2 overexpression or GFP expression (green). Note that KCC2 overexpression has no significant effect on the seizure suppression when photostimulation of PV+ interneurons is delivered immediately upon seizure detection. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; error bars represent s.e.m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file