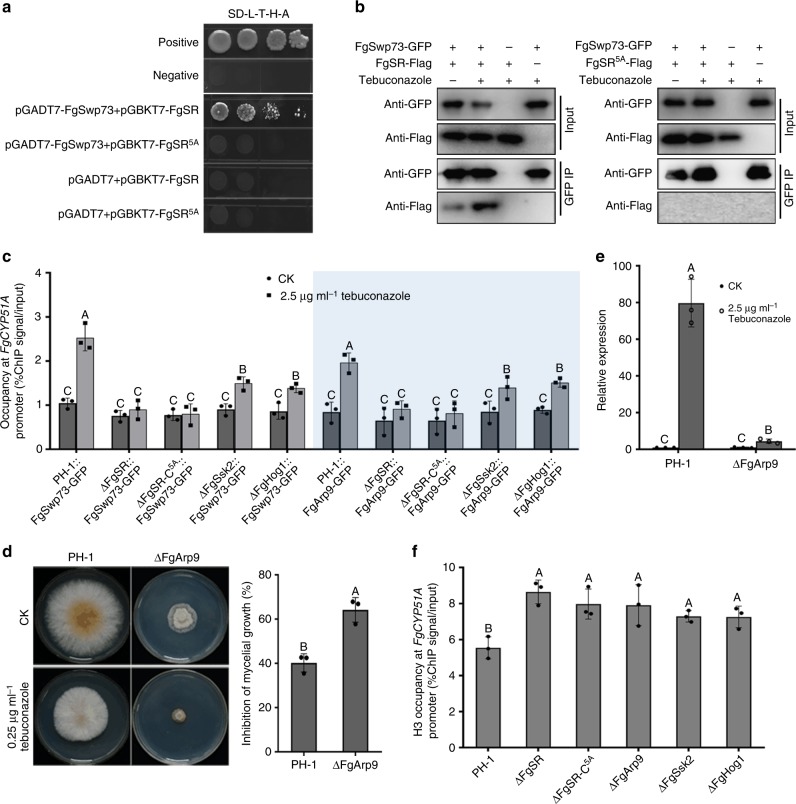
Fig. 4.
Phosphorylated FgSR interacts with the SWI/SNF complex to regulate transcription of FgCYP51A. a The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay revealed that the 5 phosphorylation residues of FgSR are critical for its interaction with FgSwp73. b FgSR interacts with FgSwp73 in the co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay. The relative strains were treated with or without tebuconazole for 2 h after incubated in YEPD for 36 h. c The enrichment of FgSwp73-GFP and FgArp9-GFP at the FgCYP51A promoter among the wild-type PH-1, ΔFgSR, ΔFgSsk2, ΔFgHog1, and ΔFgSR-C5A. ChIP- and input-DNA samples were quantified by quantitative PCR assays with the primer pair A2 indicated in Fig. 2b, and rabbit IgG was used as a control. d Deletion of the SWI/SNF complex subunit FgARP9 led to increased sensitivity to tebuconazole. A 5-mm mycelial plug of PH-1, ΔFgArp9 was inoculated on PDA alone or supplemented with 0.25 μg ml–1 tebuconazole (left panel), and the mycelial growth inhibition was calculated for each strain (right panel). e Comparisons of the expression of FgCYP51A between PH-1 and ΔFgArp9 after the treatment with 2.5 μg ml–1 tebuconazole for 6 h. The expression of FgCYP51A in the wild type without treatment was referred to 1. f The enrichment of histone H3 at the FgCYP51A promoter among the above strains. ChIP- and input-DNA samples were quantified by quantitative PCR assays with the primer pair A2 indicated in Fig. 2b, and rabbit IgG was used as a control. Data presented are the mean ± s.d. (n = 3). Bars followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to a LSD test at P = 0.01