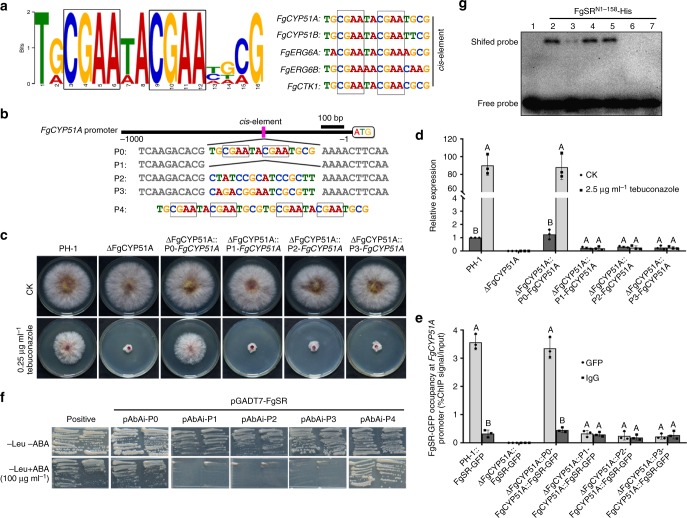
Fig. 7.
Identification of cis-element of FgSR in F. graminearum. a The putative sequence of the cis-element obtained by analyzing the promoters of five target genes with the MEME program. Two CGAA-repeated sequences within the cis-elementare indicated by the black squares. b Schematic representation of modified cis-element in the promoter of FgCYP51A. Two CGAA-repeated sequences are indicated by the black squares. c The cis-element-deleted (ΔFgCYP51A::P1-FgCYP51A) or -mutated (ΔFgCYP51A::P2-FgCYP51A and ΔFgCYP51A::P3-FgCYP51A) strains displayed increased sensitivity to tebuconazole. d In the strains ΔFgCYP51A::P1-FgCYP51A, ΔFgCYP51A::P2-FgCYP51A, and ΔFgCYP51A::P3-FgCYP51A, the expression of FgCYP51A was reduced and could not be induced by the treatment with 2.5 μg ml–1 tebuconazole. The expression level of FgCYP51A in the wild type without treatment was set to 1. e ChIP-qPCR assay revealed that FgSR could not bind to the FgCYP51A promoter lacking the cis-element or containing a mutated cis-element. ChIP- and input-DNA samples were quantified by quantitative PCR assays with the primer pair A2 indicated in Fig. 2b; rabbit IgG was used as a control. Data presented are the mean ± s.d. (n = 3). Bars followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to a LSD test at P = 0.01. f FgSR binds to the cis-element in the FgCYP51A promoter as indicated by yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) assays.The native FgCYP51A promoter (pAbAi-P0), cis-element-deleted and mutated FgCYP51A promoters (pAbAi-P1 to -P3) or the two repeats of the cis-element (pAbAi-P4) was used as a bait, and the pGADT7-FgSR as the prey. g Verification of the binding of FgSR with the cis-element by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). Lane 1 and 2, biotin-labeled motif of P0 (as indicated in Fig. 7b) without FgSRN1–158 (lane 1) or with FgSRN1–158 (lane 2); lane 3–5, biotin-labeled motif of P0 with 100 fold excess of unlabelled motif of P0 (lane 3), unlabeled mutated motif of P2 (lane 4), unlabeled mutated motif of P3 (lane 5) with FgSRN1–158; lanes 6 and 7, biotin-labeled mutated motif of P2 and P3 respectively with FgSRN1–158