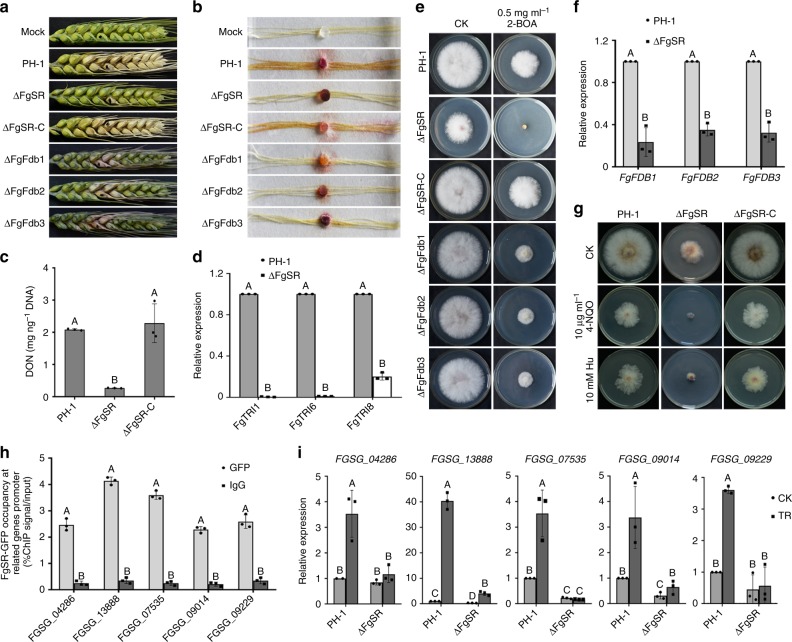
Fig. 9.
FgSR is required for virulence in F. graminearum. a Flowering wheat heads were point inoculated with a conidial suspension at 105 conidia ml–1 of each strain and infected wheat heads were photographed 15 days after inoculation (dai). b Corn silks were inoculated with mycelial plugs of each strain and examined 4 dai. c The amounts of DON (per ng DNA) produced by the wild type, ΔFgSR and ΔFgSR-C in infected wheat kernels was determined after 20 days of inoculation. d Relative expression levels of DON biosynthetic gene FgTRI1, FgTRI6, and FgTRI8 in wild type and the ΔFgSR mutant grown in TBI for two days. e Sensitivity of PH-1, ΔFgSR, ΔFgSR-C, ΔFgFdb1, −2 and −3 to the phytoalexin 2-benzoxazolinone (BOA). f FgFDB1, FgFDB2 and FgFDB3 were induced in the wild type but not in the ΔFgSR mutant after the treatment with 1 mg ml–1 BOA. The expression level of each gene in the wild type with treatment was set to 1. g Sensitivity of PH-1, ΔFgSR and ΔFgSR-C to DNA damage agent4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO) and hydroxyurea (Hu). h The enrichment of FgSR-GFP at the promoters of five genes related to DNA replication. ChIP- and input-DNA samples were quantified by PCR using primers in each gene promoter. Rabbit IgG was used in as a control. i Relative expression levels of DNA replication-related genes in PH-1 and the ΔFgSR mutant after the treatment with 50 μg ml–1 4-NQO for 4 h. The expression level of each gene in the wild type without treatment was normalized to 1. Data presented are the mean ± s.d. (n = 3). Bars followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to a LSD test at P = 0.01