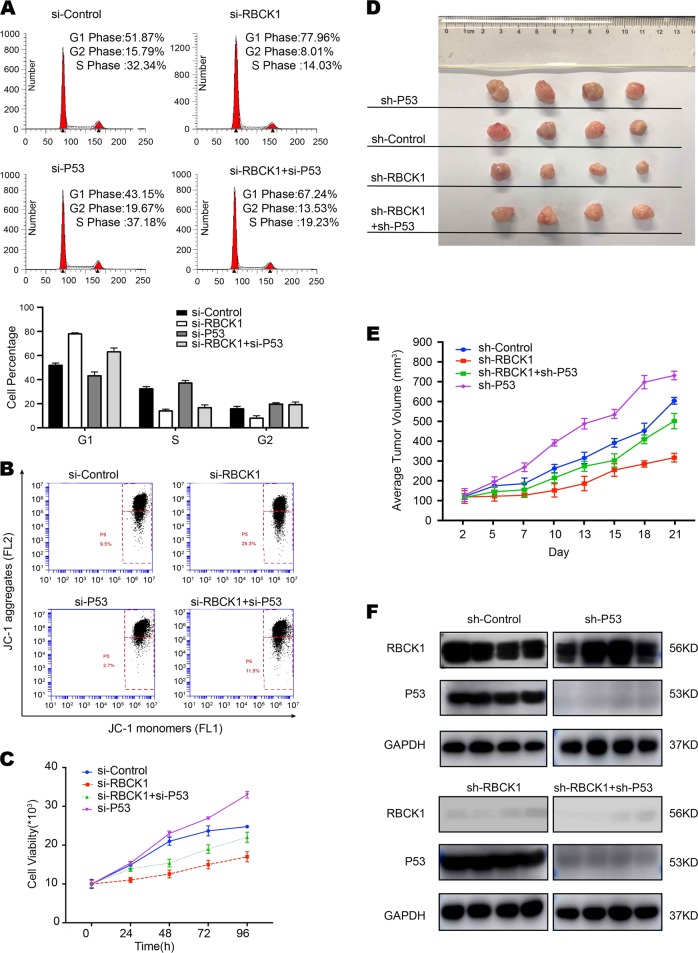
Fig. 6. Biological behavior affected by RBCK1 depletion could be rescued by p53 silencing in vivo/vitro.
a Cell cycle distribution was evaluated by flow cytometry. Caki-1 cells were transfected with control, RBCK1 siRNA,p53 siRNA or both types of siRNA (P < 0.05). Experiments were done in triplicate. b Flow cytometry was used to evaluate the MMP in four groups. Data were revealed as the monomers positive percentage of the treated Caki-1 cells to that of the untreated control. P < .05. c The CCK8 assay was used to determine the cellular metabolic activity at indicated time points after transfection. Experiments were done in triplicates in Caki-1 cells which were divided into four groups. All values are mean ± SD (n = 3, *P < .05). d Caki-1 cells were stably transfected with lentivirus carrying scramble sh-p53 or sh-RBCK1 or both shRNA. 16 NOD-SCID mice were divided into four groups. The mice were subcutaneously inoculated with cells (5 × 106 cells suspended in 100 ul PBS solution) in the logarithmic growth period. At 28 days post-injection, tumor growth was monitored every 2~3 days and the tumor volume were calculated by length × width2/2. The mice were sacrificed at 50 days after transplant. e The tumor growth curve photograph is shown. (P < .05). f Western blotting was conducted to determine the persistence of RBCK1/p53 silencing in tumor masses in 16 mice tumor tissues. GAPDH was used as an internal control