Figure 5.
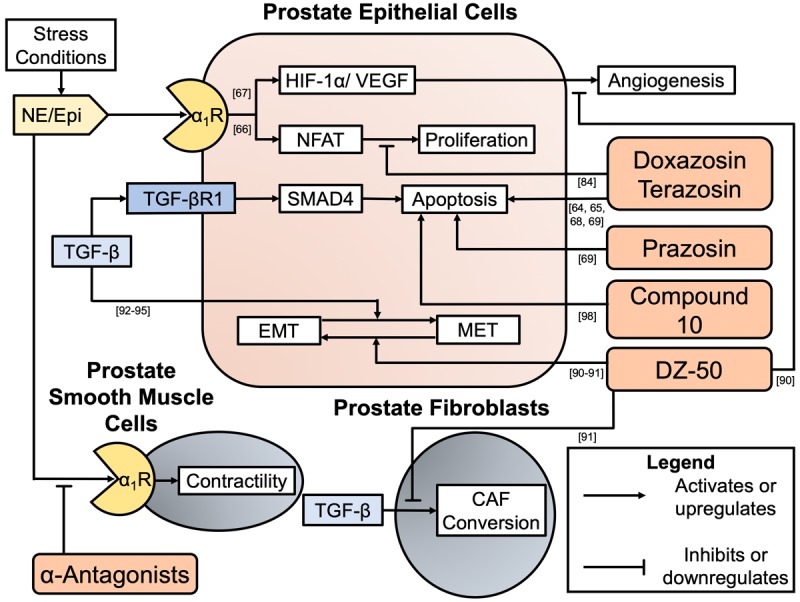
Summary of in vitro evidence demonstrating quinazoline-derived α1-adrenoceptor antagonist or modified quinazoline anti-cancer actions. Prostate epithelial-derived cancers and the microenvironment are influenced by α1-adrenoceptor antagonists. Blockade by α1-adrenoceptor antagonists at the smooth muscle cells in the prostate stroma mediate the anti-contractility benefits of the drugs when used for BPH-LUTS. Quinazoline derived α1-adrenoceptor antagonist doxazosin disrupts the proliferation axis induced by α1-adrenoceptor activation in a non-α1-adrenoceptor antagonism action ([84]). Quinazoline derived α1-adrenoceptor antagonists doxazosin, terazosin, and prazosin have demonstrated the ability to induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells ([64,65,68,69] and [69], respectively). Novel quinazoline-derived compound titled ‘Compound 10’ demonstrates anti-cancer activity with pro-oxidant DNA fragmentation in prostate cancer cell lines ([99]). Novel quinazoline-derived compound titled ‘DZ-50’ demonstrates multiple anti-cancer actions including induction of MET (reversal of EMT), inhibition of TGF-β-induced microenvironment fibroblast changes, and the inhibition of angiogenesis ([91-92], [92], and [91], respectively).
