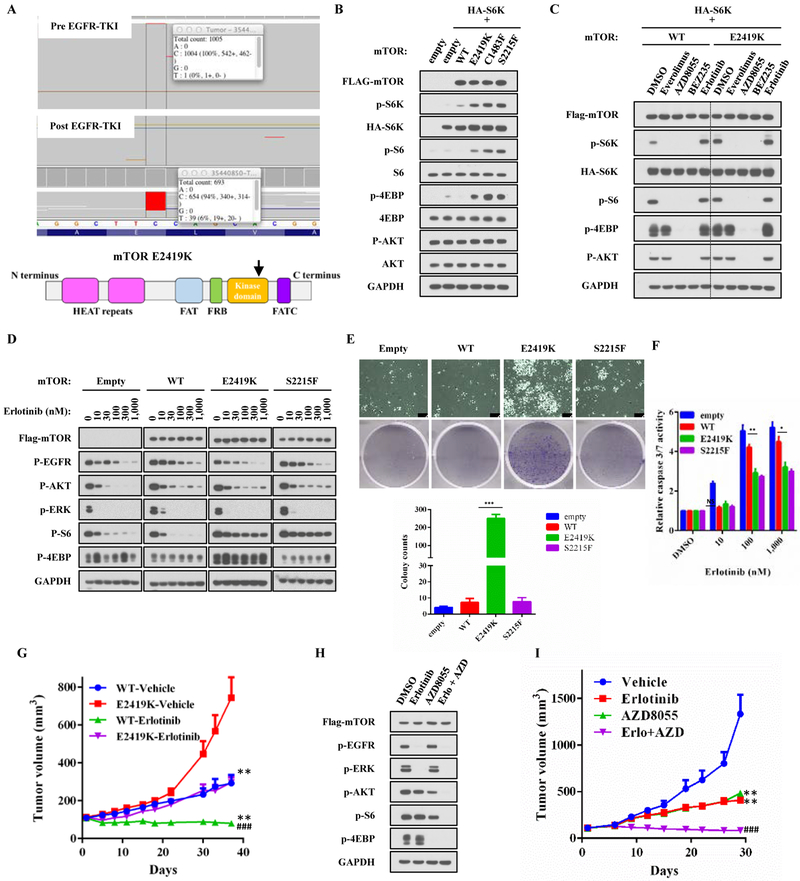
Figure 6: Functional analysis of acquired mTOR E2419K mutation in elrotinib-resistant EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer.
A. MSK-IMPACT analysis of paired samples before and after EGFR-TKI resistance revealed an acquired mTOR E2419K mutation. B. 293T cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA3 Flag-mTOR (WT, E2419K, S1483F, S2215F), vector control, or HA-S6K1. Thirty-six hours after the transfection, cells were serum starved overnight and subsequently nutrition starved in PBS for 1 hour. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting. Band intensities were quantified using ImageJ software, and data are representative of two independent experiments (mean ± SE). ***p<0.001, compared to the respective WT+S6K group. C. 293T cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA3 mTOR (wild-type, E2419K), vector control, or HA-S6K1. Forty-eight hours after the transfection, cells were treated with everolimus (100nM), AZD8055 (500nM), BEZ235 (500nM), or erlotinib (1μM) for 3 hours and then subjected to immunoblotting. D. Isogenic stable PC9-mTOR lines were treated with increasing concentrations of erlotinib for 3 hours without serum and lysates were subjected to immunoblotting. E. A total 1.5 × 104 of cells were plated in 6-well plates, and treated with 1μM erlotinib for 14 days. The number of colonies was analyzed using ImageJ. Each experiment was assayed in duplicate determinations and data are representative of three independent experiments (mean ± SE). F. Caspase 3/7 activity was analyzed in stable PC9-mTOR lines that were treated with increasing concentrations of erlotinib for 48 hours. Each experiment was assayed in duplicate determinations and data are representative of three independent experiments (mean ± SE). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared to PC9-mTOR WT group. G. PC9-mTOR WT and E2419K cells were implanted into a subcutaneous flank of athymic nude mice. When tumors reached approximately 100 mm3, mice were treated with vehicle or 25 mg/kg erlotinib daily. Tumor volume was determined on the indicated days after the onset of treatment. Data represent mean ± SE (n = 5). *p<0.05, compared to the respective vehicle-treated group. #p<0.05, compared to erlotinib-treated PC9-mTOR WT group. H. PC9-mTOR E2419K cells were treated with erlotinib (1μM), AZD8055 (500nM), or a combination of erlotinib (1μM) and AZD8055 (500nM) for 3 hours. Lysates were then subjected to immunoblotting. I. PC9-mTOR E2419K cells were implanted subcutaneously into the flank of athymic nude mice. Once tumors reached approximately 100 mm3, mice were treated with vehicle, 25 mg/kg erlotinib, 20 mg/kg AZD8055, or a combination of 25 mg/kg erlotinib and 20 mg/kg AZD8055 daily. Tumor volume was determined on the indicated days after the onset of treatment. Data represent mean ± SE (n = 5). *p<0.05, compared to the vehicle treated group. #p<0.05, compared to erlotinib only treated group.