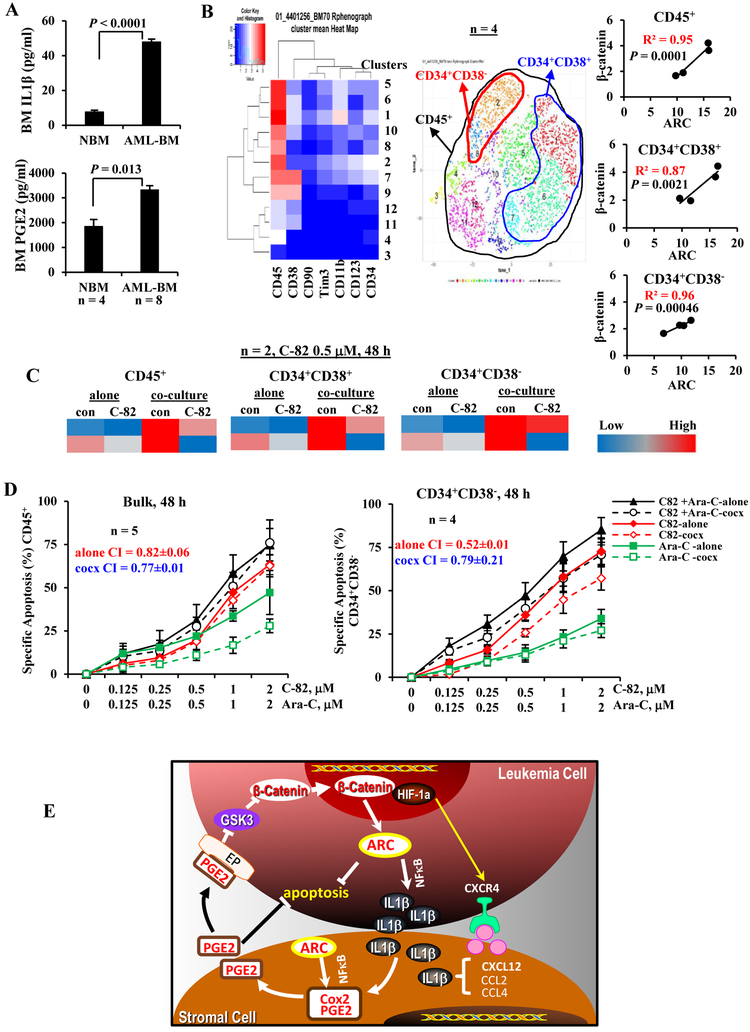
Figures 6.
PGE2/β-catenin/ARC cascade and targeting in primary AML samples and the proposed mechanism of ARC action. A. IL1β and PGE2 levels in BM samples from AML patients (n = 8) (Table 1, samples 9-16) and normal controls (NBM, n = 4) by ELISA. B. Correlation of ARC and β-catenin protein levels, determined by CyTOF in various BM cell populations of AML patients (n = 4) (Table 1, samples 17-20). C. Levels of ARC protein, determined by CyTOF in AML patient samples (n = 2) (Table 1, samples 21 and 22) treated with β-catenin inhibitor C-82 (0.5 μM) without or with MSC co-culture for 48 h. Protein levels determined by CyTOF are expressed as Arcsinh-transformed counts. D. AML patient samples were treated with C-82, Ara-C, or both for 48 h. Apoptosis was determined in blasts (n = 5) (Table 1, samples 23-27) and CD34+CD38− (n = 4) (Table 1, samples 23-26) cells. cocx, co-culture. E. Proposed mechanism of action: ARC, regulated by β-catenin, mediates leukemia stromal interaction through ARC-IL1β/Cox-2/PGE2/β-catenin circuit.