Fig. 2.
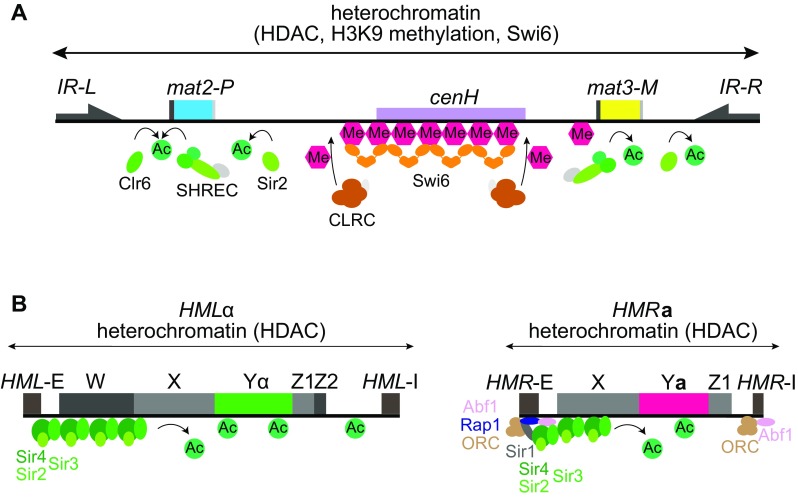
Heterochromatin at the donor loci. a In S. pombe, histone deacetylation by several HDACs (SHREC, Clr6, Sir2) together with histone H3K9 methylation by CLRC forms heterochromatin over a 20 kb domain between the IR-L and IR-R boundaries. Following histone modification, the chromodomain protein Swi6 associates with the entire 20 kb region. cenH is an RNA-interference heterochromatin nucleation center with centromere homology. b In S. cerevisiae, heterochromatin results from histone deacetylation and association of Sir proteins in two smaller domains, each < 3 kb, at the HML and HMR loci. At each cassette, the E and I silencers recruit various combinations of DNA-binding proteins, ORC, Rap1, and Abf1, to initiate heterochromatin formation
