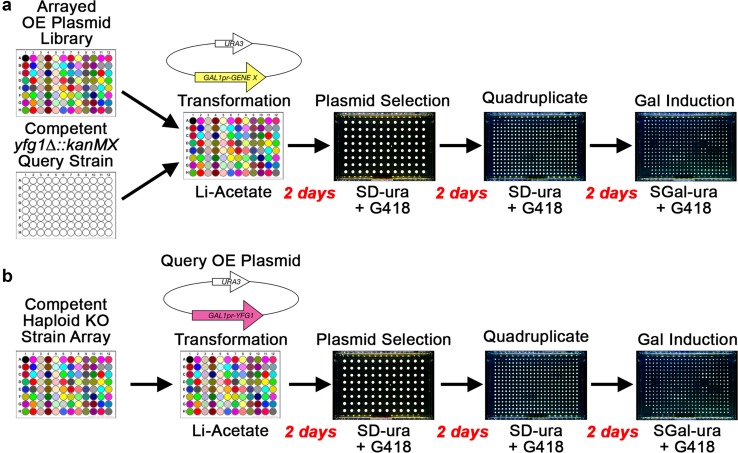
Fig. 1.
Dosage GI screens using OE plasmids. a The dosage interaction screen starts with two 96-well plates. One plate contains an arrayed OE plasmid library as DNA, each well overexpressing a different single ORF. Every well in the second plate contains the same query mutant strain denoted by your favorite gene yfg1∆. b The dosage interaction screen starts with a query overexpression plasmid and a 96-well plate containing an array of haploid deletion strains, each well containing a different deletion strain. Transformations are performed in liquid in 96-well plates. Transformants may undergo selection in liquid by transferring cells into fresh plates or by replica pinning to agar selection plates (shown). In this example, selection of the plasmid is maintained by growth on media lacking uracil (SD-ura), and selection of the gene deletions is maintained by adding G418 as the deletion collections carry kanMX. Transformants are assayed for growth under non-induced (SD-ura) and induced (SGal-ura) conditions. Transformants should be quadruplicated to 384 arrays for statistical measurements of growth. Plates are imaged and colony sizes are measured to determine if two genes interact. Red text indicates how many days are required for each step in the workflow. kanMX: G418-resistance marker, OE: overexpression, yfg1∆: deletion of your favorite gene, Gal: galactose; colored wells indicate that the contents of each well are different