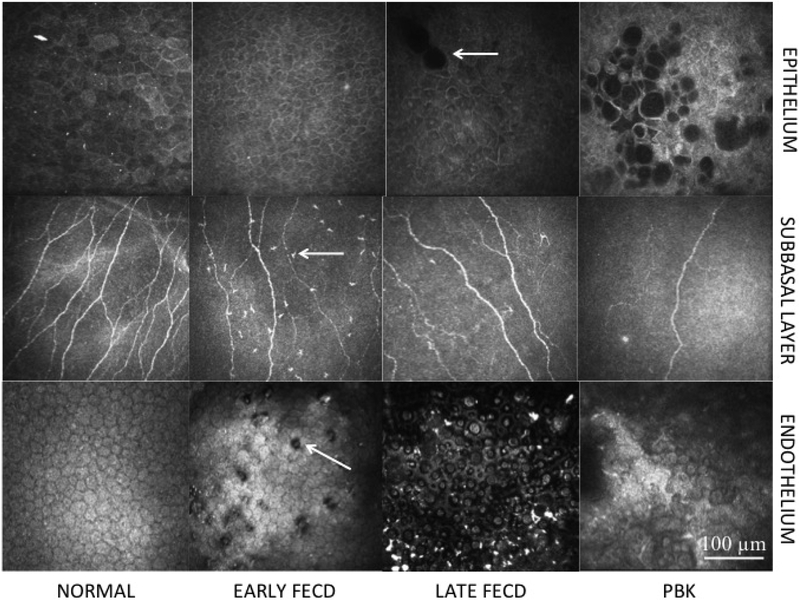
Figure 1. In vivo confocal microscopy images.
Central corneal in vivo confocal microscopy images showing the epithelium (Row 1) in normal controls (Column 1); Early stage Fuchs’ endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) (Column 2); Late stage FECD (Column 3); pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (PBK) (Column 4); subbasal layer (Row 2) in normal controls (Column 1); Early stage FECD (Column 2); Late stage FECD (Column 3); PBK (Column 4); and endothelium (Row 3) in normal controls (Column 1); Early stage FECD (Column 2); Late stage FECD (Column 3); and PBK (Column 4). Patients with early stage FECD show decreased nerves and increased immune dendritic cells (arrow) in the subbasal layer (Row 2, Column 2) and guttae (arrow) in the endothelium (Row 3, Column 2). Patients with late stage FECD show epithelial edema (arrow) (Row 1, Column 3), decreased subbasal nerves (Row 2, Column 3) and reduced endothelial density (Row 3, Column 3). Patients with PBK show epithelial edema (Row 1, Column 4), reduced subbasal nerve density (Row 2, Column 4) and reduced endothelial cell density without guttae (Row 3, Column 4). Size bar = 100μm.