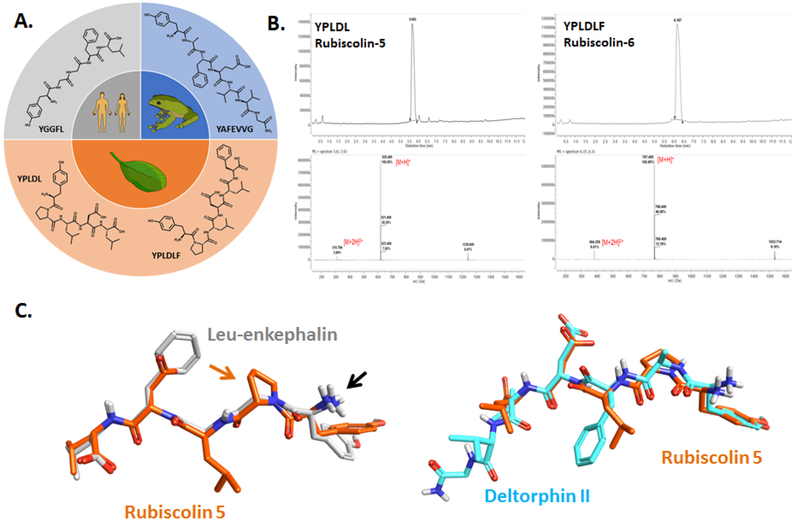
Figure 1. Origin and structural differences of naturally-occurring δ-OR peptides.
A) Chemical structures of the naturally-occurring peptides leu-enkephalin (human), [D-Ala2]-deltorphin II (frog), rubiscolin-5/YPLDL and rubiscolin-6/YPLDLF (spinach). B) HPLC-MS spectra for rubiscolin-5 and rubiscolin-6. C) Maximum common structure alignment for rubiscolin-5 (orange) with leu-enkephalin (gray) or deltorphin II (cyan). Black arrow points to the conserved amino-group. Orange arrow points to the proline residue unique to the rubiscolins.