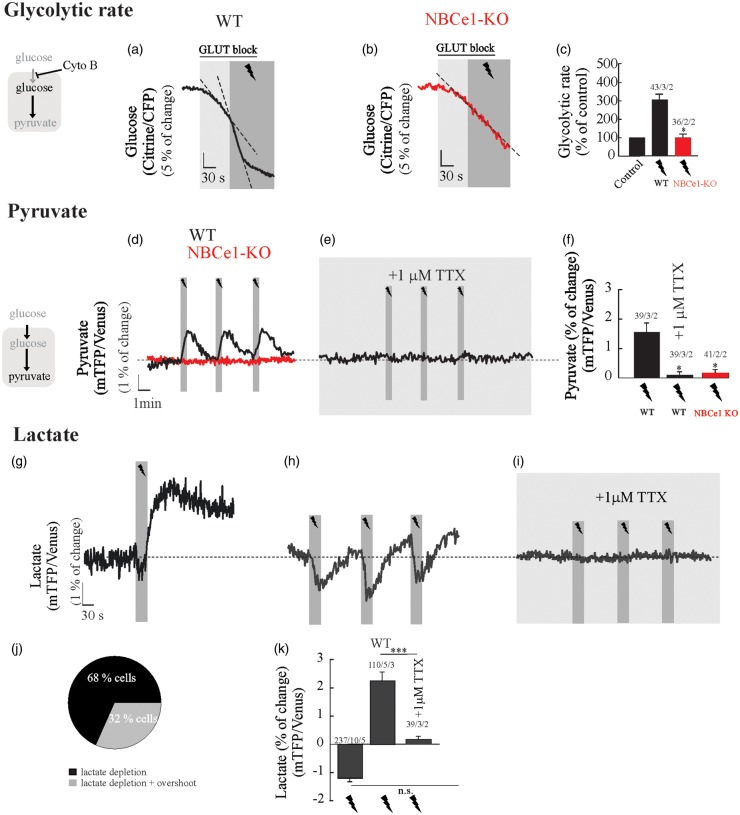
Figure 4.
NBCe1 is required for fast glycolytic activation and a rise in pyruvate in hippocampal astrocytes challenged by neuronal stimulation. Glucose, pyruvate and lactate imaging in astrocytes from OHS perfused with HCO3−/CO2 saline containing 2 mM glucose and 1 mM lactate. (a–c) Cytochalasin B (20 µM) was applied to block glucose transporters and determine the effect of neuronal stimulation on astrocytic glucose consumption in WT and NBCe1-KO astrocytes. (d–f) Effect of Schaffer collateral stimulation (20 Hz, 30 s) on intracellular pyruvate of astrocytes from WT and NBCe1-KO astrocytes perfused with HCO3−/CO2 saline containing 2 mM glucose and 1 mM lactate in the presence or absence of 1 µM TTX in wild-type. (g–i, k) Effect of Schaffer collateral stimulation (20 Hz, 30 s) on intracellular lactate in astrocytes perfused with HCO3−/CO2 saline containing 2 mM glucose and 1 mM lactate in the presence or absence of 1 µM TTX in wild-type. (j) Pie chart representing the distribution of lactate responses in WT astrocytes challenged to neuronal stimulation. All traces represent individual astrocytes. Bar graphs summarise the percentage of change of glucose, pyruvate or lactate FRET sensors upon stimulation/TTX in astrocytes from WT and NBCe1-KO hippocampal slices. The number of experiments is represented as n° of cells/ n° slices/ n° animals.