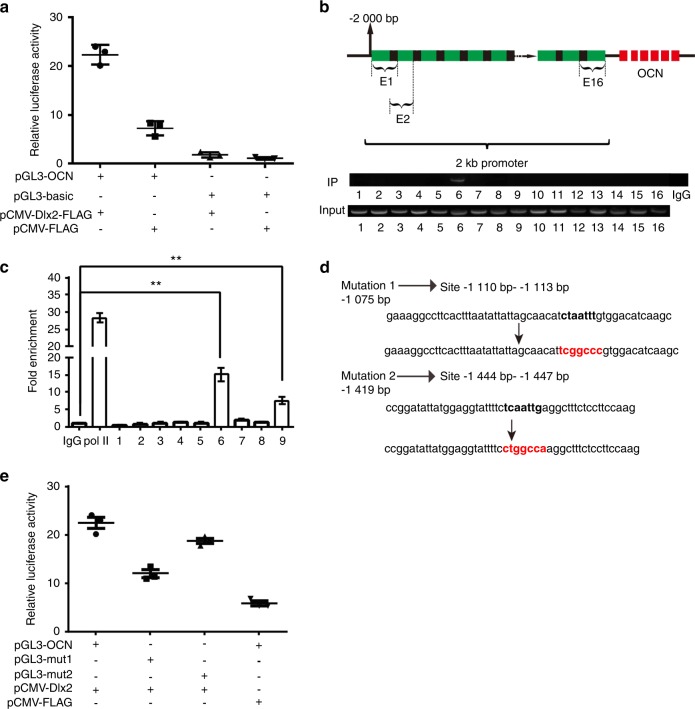
Fig. 5.
Characterization of the mouse OCN promoter and identification of its Dlx2-response elements. a The basal luciferase activity of the whole OCN promoter construct (pGL3-OCN) and that of the empty (pGL3-basic) construct in MC3T3-E1 cells was determined by transfecting the cells with each promoter reporter construct along with the Dlx2 overexpression vector (pCMV-Dlx2-FLAG) or the empty vector (pCMV-FLAG). Cells were then harvested 24 h after the transfection, and luciferase activity was measured and normalized to the protein concentration in the cell lysate. b ChIP analysis was performed to determine the Dlx2-response elements in the OCN promoter. MC3T3-E1 cells were transfected with pCMV-Dlx2-FLAG. Semi-quantitative PCR was performed using overlapping and closely spaced primer pairs to dissect the whole OCN promoter region into 16 short (~ 175 bp) overlapping parts for identification of the bound protein. Normal IgG (2 μg) was used as control. The PCR products were then separated by electrophoresis through a 2% agarose gel. c ChIP analysis followed by RT-qPCR was performed using the same primers described in b. Statistical significance was determined as described in Fig. 1. d The sequences of the nucleotides whose sequences contain the AATT element in the OCN promoter and the sequences of two mutants. The mutant binding sites are marked in red, and the putative Dlx2-binding sites are indicated in parentheses. e The luciferase activity of wild-type OCN promoter constructs (pGL3-OCN) and the mutated ones (pGL3-mut1 and pGL3-mut2) were determined by transfecting these vectors into MC3T3-E1 cells along with pCMV-Dlx2-FLAG or pCMV-FLAG. The OCN promoter construct bearing approximately −2000 to 0 bp region was subjected to site-directed mutagenesis to substitute the AATT sequence (pGL3-OCN) with either mutation1 (pGL3-mut1) or mutation2 (pGL3-mut2). The luciferase activity was measured 24 h later