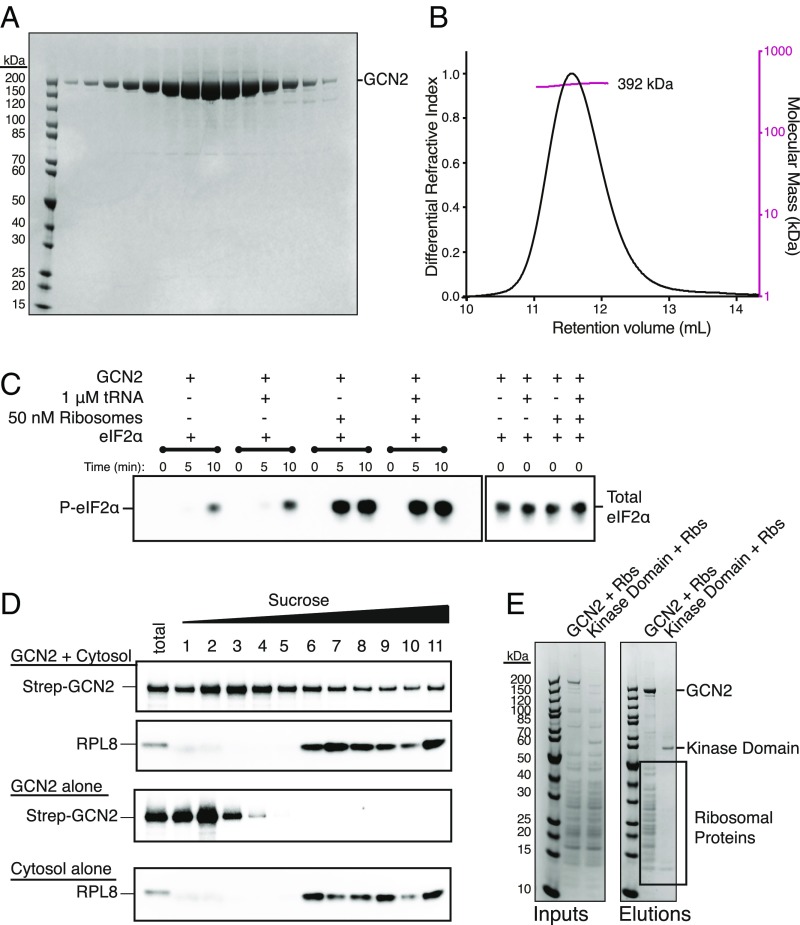
Fig. 1.
Purified ribosomes are a potent activator of GCN2. (A) SDS/PAGE analysis of gel filtration fractions for purified human GCN2 stained with Coomassie Blue. (B) Size-exclusion chromatography–multiangle light scattering (SEC-MALS) profile of GCN2. The molecular weight measured by light scattering was 392 kDa, consistent with a dimeric state. (C) eIF2α phosphorylation assay. The reactions were assembled and started by the addition of ATP. Samples were taken at 0, 5, and 10 min. The reactions were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against phospho-eIF2α (P-eIF2α) and total eIF2α. (D) Migration of GCN2 through a sucrose gradient in the presence and absence of cytosol (rabbit reticulocyte lysate). The sample identities are shown on the Left. The reactions were incubated for 15 min before being run over a 10–50% sucrose gradient. Eleven fractions were collected and analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Western blotting with either an anti-StrepII tag or anti-RPL8 antibody. (E) Pulldown analysis of the GCN2–ribosome interaction. Either full-length GCN2 or the kinase domain only (residues 585–1,024) were incubated with purified ribosomes and the resultant complexes captured on StrepTactin resin. The beads were washed and the proteins eluted in sample buffer. The elutions were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie staining. The bands corresponding to GCN2, the kinase domain, and ribosomal proteins are indicated on the Right.