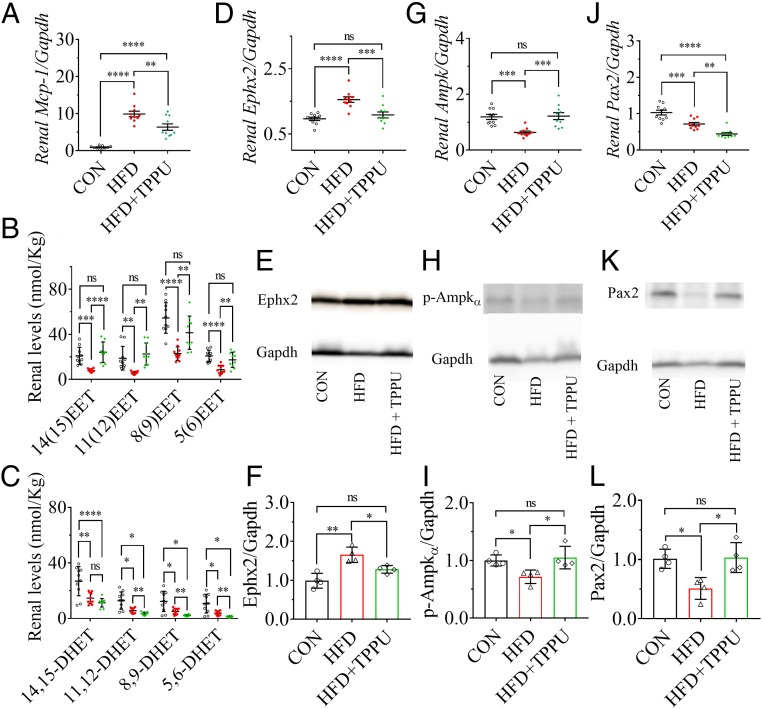
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of sEH by pharmacological intervention with the sEH inhibitor TPPU attenuated the HFD-mediated renal injury by activating Pax2 and Ampk. (A) Treatment with TPPU significantly reduced the HFD-induced renal mRNA level of Mcp-1. (B) TPPU treatment markedly increased HFD-induced decrease in renal levels of 14(15)-, 11(12)-, 8(9)-, and 5(6)-EET while (C) TPPU significantly decreased HFD-induced decrease in renal levels of 11,12-, 8,9-, and 5,6-DHET. Renal mRNA levels of (D) Ephx2, (G) Ampk, and (J) Pax2 were significantly modified by TPPU treatment; Western blot analysis and quantitation of the band density of (E and F) Ephx2, (H and I) p-Ampkα, and (K and L) Pax2. Unfilled circles, red dots, and green triangles represent the individual mouse treated with a CTD, an HFD, and an HFD with TPPU, respectively. Data represent mean ± SEM for A–C, D, G, and J (n = 10), and mean ± SD for F, I, and L (n = 4). The Western blot analysis and quantitation of the band density of p-Pax2 (Ser-393) is presented in SI Appendix, Fig. S7 A and B, which shows a similar pattern to Pax2; ns (no significant difference) P ≥ 0.05, 0.01 < *P < 0.05, 0.001 < **P ≤ 0.01, 0.0001 < ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001 were determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s or Games−Howell post hoc comparison test.