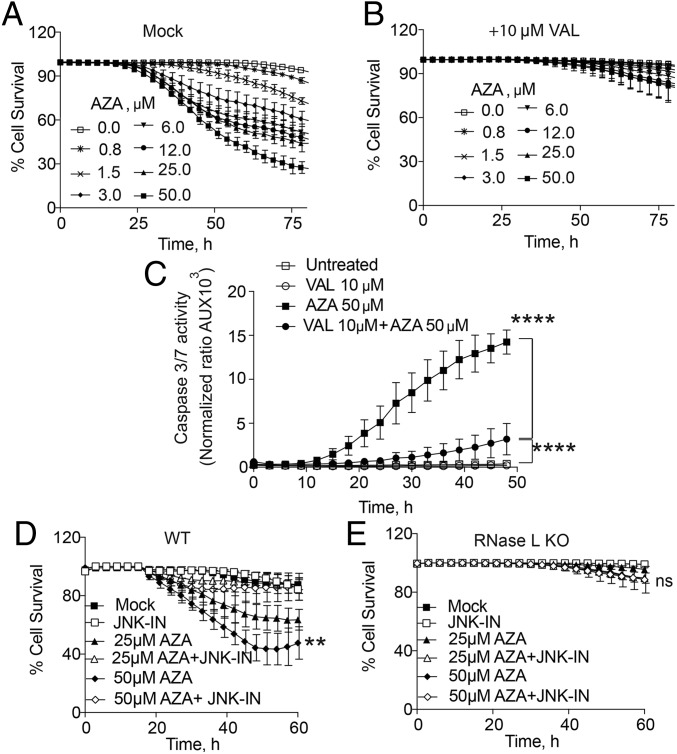
Fig. 4.
Small-molecule inhibitors of either RNase L or JNK inhibit AZA-induced cell death. (A and B) Percent survival of WT A549 cells after AZA treatment in the (A) absence or (B) presence of the RNase L inhibitor VAL. Data are the averages ± SD from five identically treated replicates. Three biological replicates were performed, each with a minimum of three technical replicates. (C) Caspase-3/7 activity in A549 cells in the presence or absence of AZA and VAL. Data are the averages ± SD from three identically treated replicates. Two biological replicates were performed. (D and E) Percent cell survival of WT and RNase L KO A549 cells, respectively, mock-treated or treated with 25 µM SP600125 (JNK inhibitor; JNK-IN) for 2 h and then incubated with AZA (25 or 50 μM). Data are the averages ± SD from five identically treated replicates. Four biological replicates were performed, each with a minimum of three technical replicates. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant.