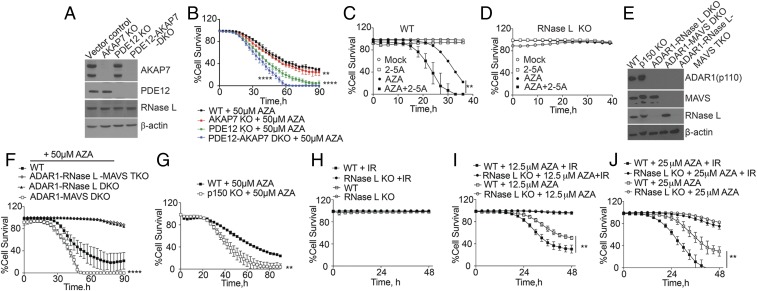
Fig. 5.
Effect of RNase L on cell death during AZA treatment is increased by (A and B) KO of PDE12 and/or AKAP7, (C and D) 2-5A transfection, (E–G) KO of ADAR1 or its p150 isoform, or (H–J) IR. (A) Western blots of vector control WT, AKAP7 KO, PDE12 KO, and PDE12-AKAP7 DKO A549 cells, probed with the indicated antibodies. (B) Percent cell survival of WT, AKAP7 KO, PDE12 KO, and PDE12-AKAR7 DKO cells after AZA treatment. The data are the averages ± SD of three identical replicates. Three biological replicates were performed, each with a minimum of three technical replicates. (C and D) Percent survival of WT and RNase L KO cells with and without 1 μM 2-5A transfection. (E) Western blots of WT, ADAR1 p150 KO, ADAR1-RNase L DKO, ADAR1-MAVS DKO, and ADAR1-RNase L-MAVS TKO cells. (F and G) Percent cell survival after AZA treatment. The data are the averages ± SD of three identical replicates. Three biological replicates were performed, each with a minimum of three technical replicates. (H–J) Percent cell survival after IR (10 Gy) for 30 min, followed by AZA treatment in comparison with mock treatments. The data are the averages ± SD of three identical replicates. Two biological replicates were performed, each with a minimum of three technical replicates. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.