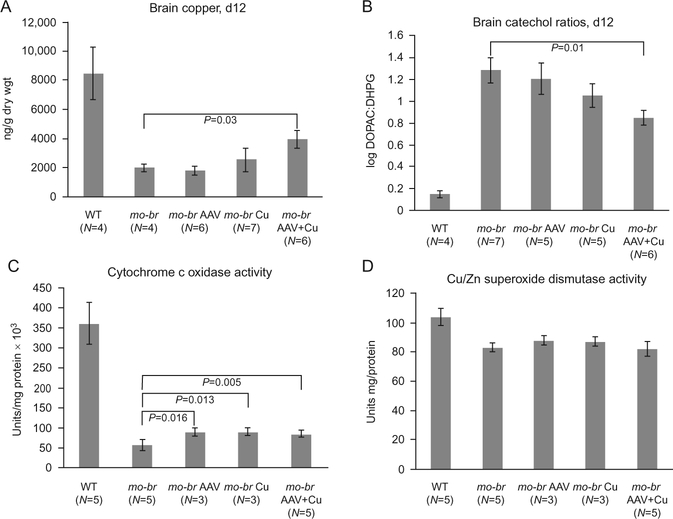
Figure 11.7.
Biochemical effects of brain-directed treatment in the mottled-brindled (mo-br) model of Menkes disease. (A) Brain copper levels at 12 days of age, by treatment category. Only AAV5 + copper (Cu) combination-treated mo-br mice showed significantly higher copper levels in comparison to untreated mo-br mice (P<0.03). (B) Brain catechol ratios at 12 days of age, by treatment category. Only AAV5+Cu combination-treated mo-br mice showed significantly lower ratios, indicative of improved dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity (P<0.01). (C) Brain cytochrome c oxidase activity at 12 days of age, by treatment category. All treatment groups showed significantly increased activity compared to untreated mo-Br mice. (D) In contrast, the activity of Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase was ~80% of normal and treatment did not significantly enhance activity. Reproduced from Donsante et al. (2011), with permission.