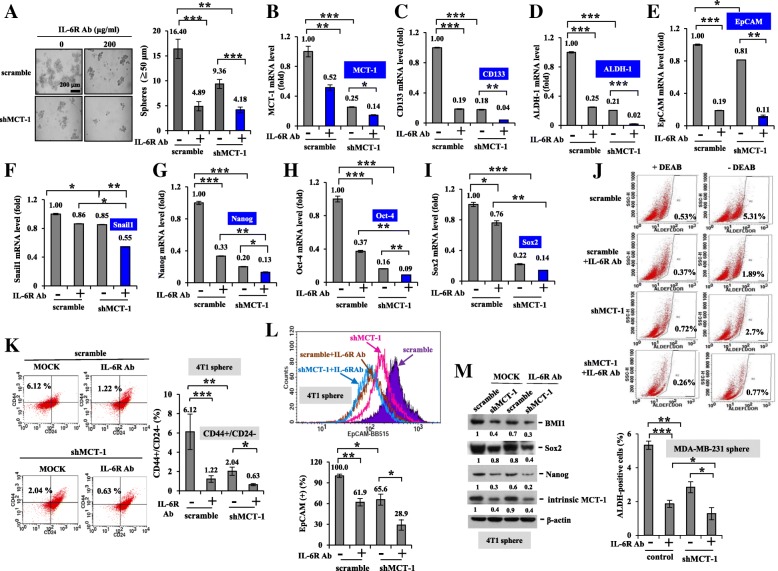
Fig. 5.
Tocilizumab and shMCT-1 synergistically inhibit breast cancer stemness. (a) The mammospheres derived from IV2–3 subline (scramble vs. shMCT-1#3) were evaluated upon tocilizumab (200 μg/ml) treatment for 20 days. The mRNA levels of the indicated gene were examined in MDA-MB-231 mammospheres and after tocilizumab challenge. (b) MCT-1. (c) CD133. (D) ALDH-1. (e) EpCAMP. (f) Snail. (g) Nanog. (H) Oct-4. (i) Sox2. (j) ALDH(+) cancer stem cells were detected by an ALDEFLUOR assay as DEAB inhibited ALDH activity, to accurately analyze ALDH activity in day 14 mammospheres and after tocilizumab treatment. (k) CD44-FITC and CD24-Alexa staining identified CD24(−)/CD44(+) subpopulations in the 4 T1 mammospheres (scramble and shMCT-1#3–28) and upon tocilizumab treatment for 6 days. (l) EpCAM(+) cancer stem cells were evaluated in the 4 T1 mammospheres and upon tocilizumab treatment for 6 days using EpCAM-BB515 staining. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with a post hoc two-tailed t-test was used to calculate the statistical significance of pairwise comparisons. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001) (m) The cancer stemness molecules in scramble and shMCT-1#3–28 cells were examined before and after tocilizumab treatment