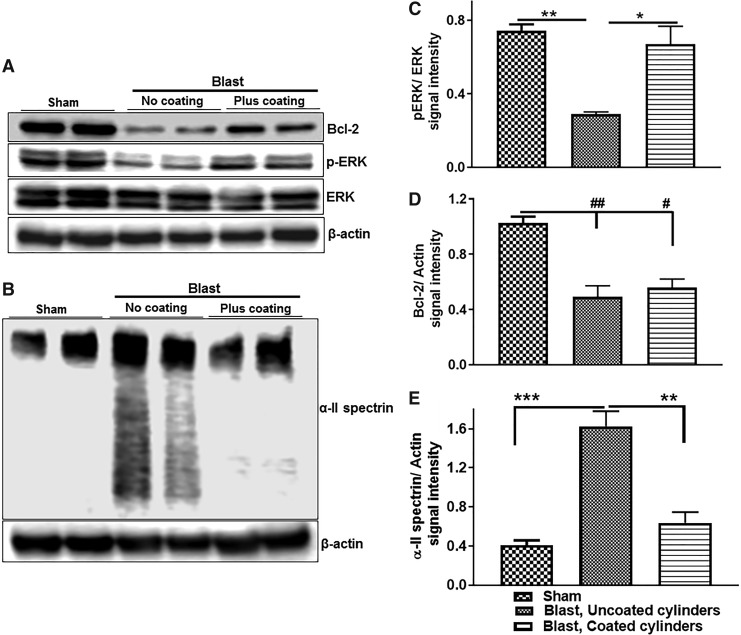
FIG. 9.
Decreased expression of cell survival promoting proteins and increased expression of pro-apoptotic protein in rat hippocampus 24 h post-blast, and mitigation by the shock-absorbing hull design system. (A,B) Representative immunoblots illustrating the expression of cell survival promoting protein phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and pro-apoptotic marker α II spectrin in rat hippocampus. (C–E) Quantitation of protein band signal intensity showed, compared with sham rats, a significant decrease in phospho-ERK and Bcl-2 (n = 6, **,##p < 0.01), and a drastic increase in α ii spectrin (n = 6, ***p < 0.001) in the hippocampus of rats exposed to lethal blast intensity with no polyurea coating compared with sham rats. Rats subjected to blast with advanced hull mitigation design still showed significantly lower Bcl-2 expression levels than shams (n = 6; #p < 0.05). However, the advanced hull mitigation design abrogated the deleterious effect of blast exposure on the expression phospho-ERK and α II spectrin (n = 6; *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01, respectively).