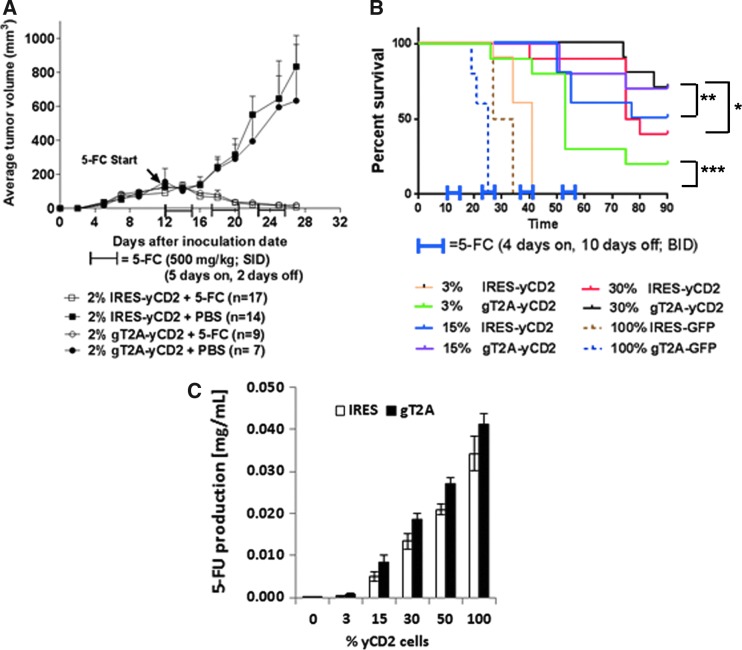
Figure 5.
Tumor burden and survival analysis of Tu2449 tumor mouse models. (A) Tumor burden of female B6C3F1 mice subcutaneously implanted with 1 × 106 cells mixed with 2% Tu2449SC/RRV-IRES-yCD2 + 98% Tu2449SC tumor cells or 2% Tu2449SC/RRV-gT2A-yCD2 + 98% Tu2449SC tumor cells on the right flank. On day 12, 5-FC treatment (arrow, 500 mg/kg in 800 μL intraperitoneally [i.p.], once daily [SID]) was administered in three cycles: 5 days on followed by 2 days off; or PBS treatment (800 μL i.p., SID) in parallel, through 30 days post tumor inoculation. Tumor sizes were monitored two to three times a week until tumor volumes reached >2000 mm3. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA of the following data sets: p < 0.0001 for g2A-yCD2 + 5-FC vs. g2A-yCD2 + PBS; p < 0.0001 for IRES-yCD2 + 5-FC vs. IRES-yCD2 + PBS. (B) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of orthotopic glioma mouse model. B6C3F1 mice were implanted intracranially (i.c.) with the different ratios of Tu2449/RRV-IRES-yCD2 to Tu2449/RRV-IRES-GFP or Tu2449/RRV-gT2A-yCD2 to Tu2449/RRV-2A-GFP cells (3/97, 15/85, and 30/70, respectively) then dosed i.c. with vehicle (control, PBS) or i.c. with 5-FC, starting at 10 days post tumor implant over four cycles of 4 days on 5-FC followed by10 days off, treated twice daily. Survival analysis was monitored for 90 days. Statistical significance of survival between mice treated with RRV-IRES-yCD2 and RRV-gT2A-yCD2 for each subgroup was determined by the log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test and is indicated by brackets: *p = 0.1416; **p = 0.3755; ***p = 0.0013. (C) Measurement of extracellular 5-FU concentrations generated from the conversion of 5-FC to 5-FU by the yCD2 proteins. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the data set.