Figure 10.
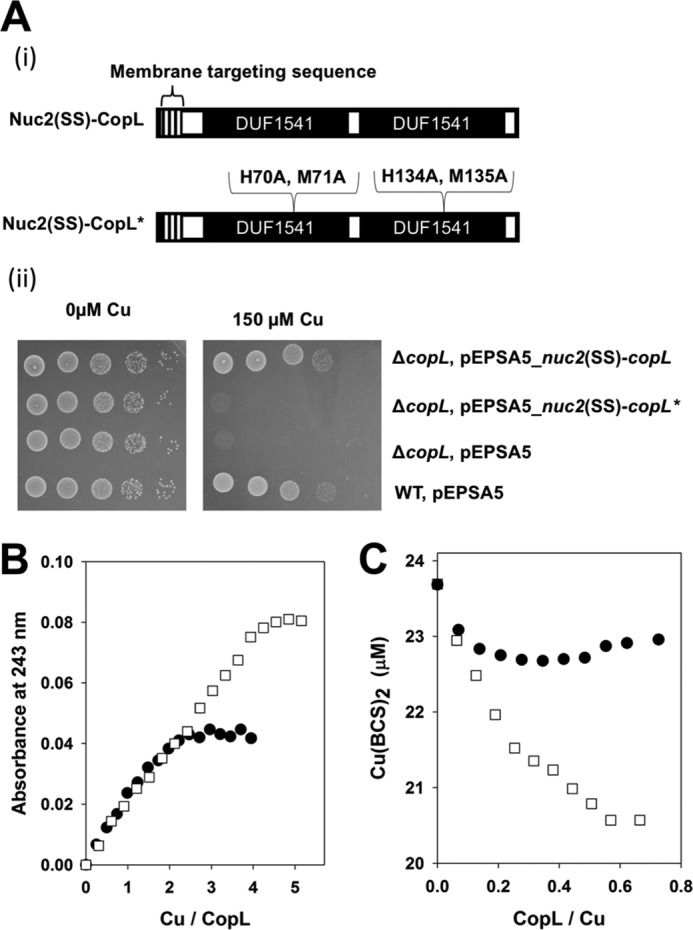
Effective Cu binding is necessary for CopL to protect against Cu toxicity. A, copL* allele does not correct the Cu sensitivity phenotype of the S. aureus ΔcopL mutant. Panel i, schematic of the copL and copL* constructs utilized. Panel ii, WT and ΔcopL strains harboring pEPSA5, pEPSA5_nuc2(SS)-copL, or pEPSA5_nuc2(SS)-copL* were serially diluted and spot-plated on chemically defined media without and with 100 μm Cu. B, saCopL(T)* binds less Cu1+ than saCopL(T). 12.5 μm apo-saCopL(T) or apo-saCopL(T)* were anaerobically titrated with Cu1+. Binding was monitored by measuring absorbance at 243 nm using UV absorption spectroscopy. C, saCopL(T)* has a lower affinity for Cu1+ than saCopL(T). Solutions containing 0.5 mm BCS and 20 μm Cu1+ were titrated with either apo-saCopL(T) or apo-saCopL(T)*. Copper binding to CopL was examined using BCS displacement by monitoring sample absorbance at 483 nm, which is the absorption maxima for the Cu1+–BCS complex. The data for the saCopL(T) are also presented in Fig. 6 and included here for comparison.
