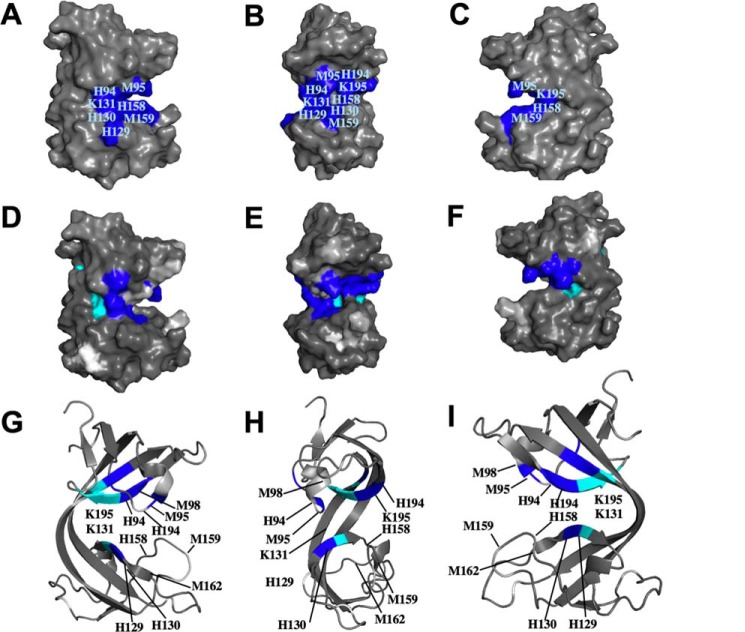
Figure 9.
Cu1+ binding to B. subtilis CopL. A–C, surface molecular representation of B. subtilis CopL, in three orientations, showing the locations of conserved residues His-94, Met-95, Met-98 (buried), His-129, His-130, Lys-131, His-158, Met-159, Met-162 (buried), His-194, and Lys-195, presumed to be involved in coordinating Cu1+. Only residues that can be seen on the surface of the 3D structure are labeled. D–F, surface representation of B. subtilis CopL, in same three orientations, showing chemical shift perturbations due to Cu1+ binding. Color code: dark blue (ΔδNH >0.25 ppm, viz. Thr-92, Met-95, His-130, His-131, Met-179, Val-180, Asn-193, His-194, Lys-195); cyan, residues with HN resonances that are broadened due to Cu1+ binding (viz. Trp-132, Tyr-178, Trp-196, Val-197, and Thr-198); light gray, residues with HN resonances that are absent in the 15N,1H HSQC spectrum of apo-CopL and not assigned (viz. Lys-83, His-94, Lys-96, Gly-97, Lys-160, Gly-161, and Ser-187); and white for proline residues that lack backbone amide protons (viz. Pro-120 and Pro-148). G–I, ribbon representation of B. subtilis CopL, in same three orientations, showing conformational perturbations due to Cu1+ binding using the same color code as in D–F. G–I, only the residues with HN resonances that are affected by Cu1+ binding are labeled. The numbering shown here is that of the UniProt entry BSU05790.