Figure 7.
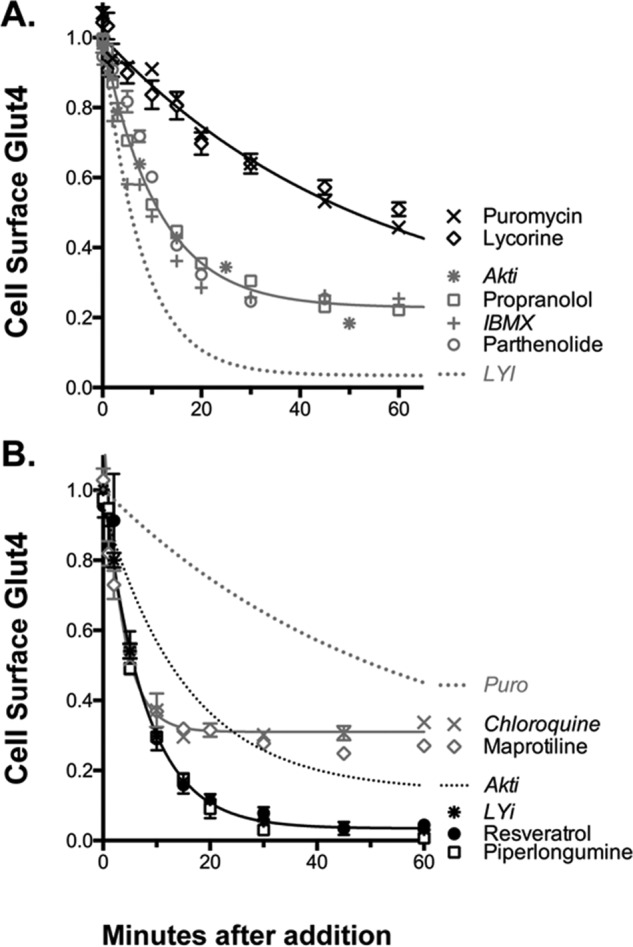
Mechanism of action of inhibitors, time course. Cells were treated as described in Fig. 4. The shapes of the curves distinguish four different mechanisms (summarized in Table 3). A, protein synthesis inhibitors (slow, 80%; e.g. puromycin) and inhibitors of signal transduction (intermediate, 80%; e.g. Akti). B, inhibitors of Glut4 exocytosis (fast, 80–90%; e.g. LYi) and inhibitors of endosomal acidification (very fast, 50%; e.g. chloroquine).
