Fig. 2.
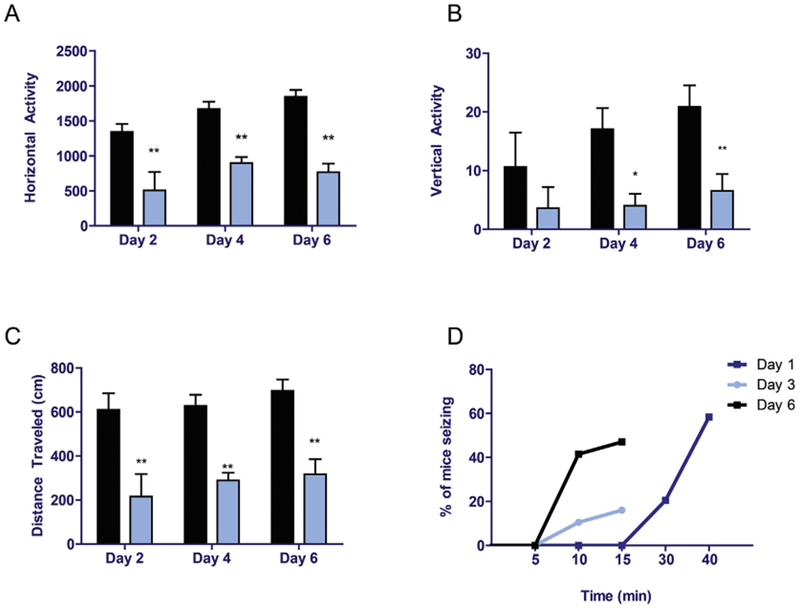
Acute exposure to hydrogen sulfide induced motor deficits and seizures.
C57 black mice were exposed to H2S as shown in Fig. 1. Locomotor activity was measured using an automated VersaMax locomotor activity monitor for 10 min on days 2, 4, and 6. Horizontal activity (A), vertical activity (B), and total distance traveled (C) were analyzed between groups. For seizures, time to seizure and number of mice seizing were monitored (D). Asterisks (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01) indicate statistically significant differences between H2S and breathing air negative control groups.
