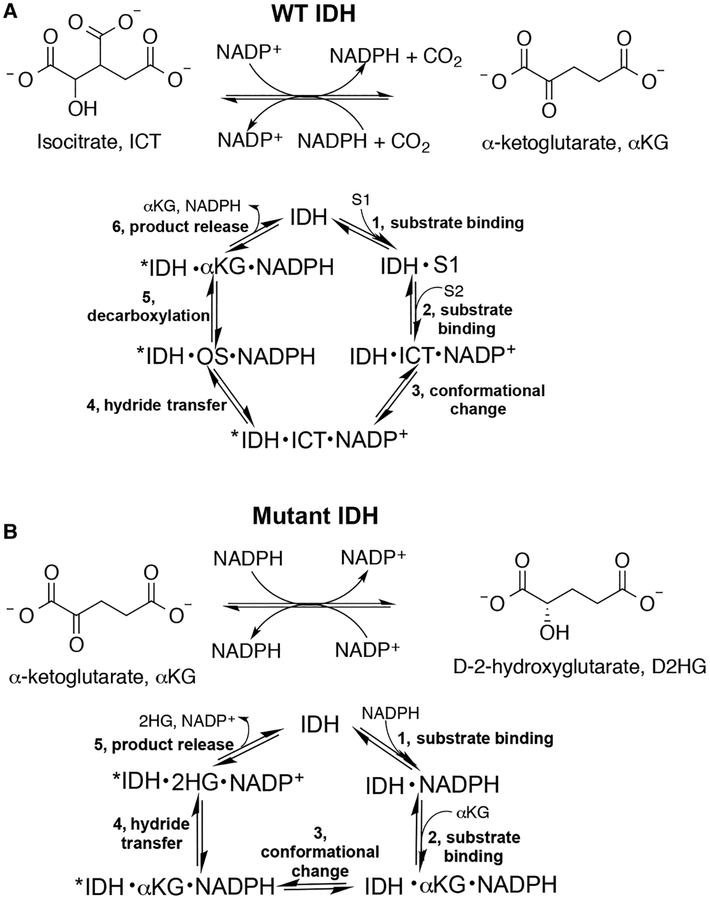
Figure 1. Reactions catalyzed by WT and mutant IDH1.
(A) WT IDH1 catalyzes the reversible, NADP+-dependent oxidation of ICT to αKG (OS, oxalosuccinate). (B) Mutant IDH1 is typically deficient in the normal reaction shown in (A) and instead acquires a neomorphic reaction, the NADPH-dependent reduction in αKG to generate the oncometabolite, D2HG [10]. For both reactions, the predicted catalytic cycle is also shown.