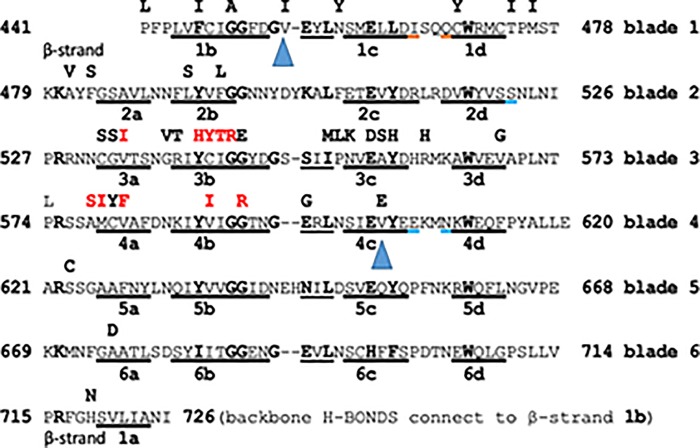
Fig 2. Sequence alignment for the Pfk13 propeller using 4YY8b and S-S 4ZGCa models.
Alignment of the 6 Kelch propeller blades of K13 as predicted by in silico modelling (structures RCSB 4YY8b and 4ZGCa with a Cys532-Cys580 link; [25, 26]); inter-blade residue similarities are emphasised in bold. Each of the β-strands in each blade is underlined and presented in order of the sequence. After the 6th blade, the terminal β-strand 1a binds at the start to complete the propeller structure before β-strand 1b. The characteristic kelch markers L-W, Y-W, Y-W, Y-W, Y-W and F-W occur in each blade and each span 6 intervening residues. Individual residue replacements are seen in bold above each blade. Ten variant residues depicted in red were seen to promote the Cys 532-Cys 580 link in 4YY8b and prevent it in 4ZGCa, when tested using the SDM (2011) suite. In Cys-Cys–linked 4ZGCa the illustrated β-strand includes the brown-underlined residues, and excludes the blue-underlined residues. In all predicted structures, the basic Arg or Lys residues in position 2 of each row contribute their protonated side chain N atom(s) to form a ring of charge around the lower entrance of the propeller channel. Each of the 2 mutations V454I and V603E is underlined by a triangular blue marker.