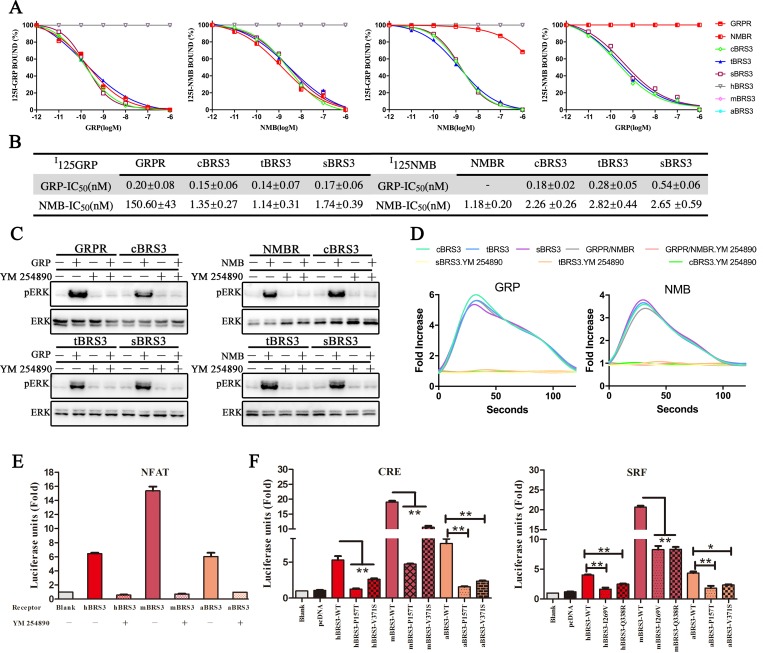
Fig 3. GRP and NMB directly bind to BRS3 in nonplacental vertebrates in high affinity via Gq signaling, whereas BRS3 in placental mammals constitutively activates two novel G protein–signaling Gs and G12.
(A) Binding of GRP and NMB to BRS3 receptors in nonplacental vertebrates. (B) Comparison of binding affinity of GRP/NMB to BRS3, GRPR, and NMBR receptors. “-” indicates not detected. Values represent IC50 expressing as mean ± SE for at least three independent experiments. (C) YM 254890 inhibits the phosphorylation levels of ERK for BRS3 receptors in nonplacental vertebrates. Receptor-expressing HEK293 cells were pretreated with inhibitor for 1 h with 25 μM. Subsequently, GRP or NMB peptides were added to the cells at a concentration of 1 μM for 5 min before western blot. (D) YM 254890 inhibits Ca2+ ion levels in cells transfected with BRS3 receptors of nonplacental vertebrates. Receptor-expressing HEK293 cells were pretreated with inhibitor for 1 h with 25 μM. Subsequently, GRP or NMB were added to the cells at a concentration of 10 nM prior to the assay. The calcium fold is calculated by fluorescence intensity (excitation/emission wavelength: 490/520 nm). (E) YM 254890 inhibits the constitutively activated Gq signaling pathway with BRS3 of placental mammals. Receptor-expressing HEK293 cells were pretreated with 25 μM inhibitor for 12 h prior to the luciferase assays. (F) Constitutive activity for each BRS3 mutants in placental mammals. Statistical significance was defined as a P value < 0.05 (*) or P value < 0.01 (**). The underlying data can be found in S2 Data. aBRS3, aardvark BRS3; BRS3, bombesin receptor subtype-3; cBRS3, chicken BRS3; CRE, cAMP response element; ERK, extracellular signal–regulated kinase; GRP, gastrin-releasing peptide; GRPR, GRP receptor; hBRS3, human BRS33; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293; mBRS3, mouse BRS3; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NMB, neuromedin B; NMBR, NMB receptor; pERK, phosphorylated ERK; sBRS3, spotted gar BRS3; SRF, serum response factor; tBRS3, turtle BRS3.