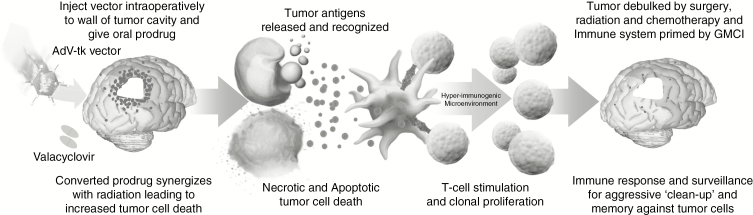
Fig. 1.
Schematic of GMCI mechanism of action. GMCI synergizes with surgery and radiation, generating activated T cells that kill tumor cells left after tumor debulking by SOC. The GMCI mechanism includes 3 steps to induce an antitumor immune response: (1) AdV-tk (aglatimagene besadenovec) in tumor cells converts valacyclovir prodrug into nucleotide analogs that kill tumor cells, releasing tumor associated antigens; (2) the presence of the injected virions and the cell death through both necrosis and apoptosis generate “danger signals” which attract and stimulate antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells; and (3) the vector-expressed TK protein functions as a super-antigen that leads to a hyper-immunogenic microenvironment with STING pathway activation and production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-12, with consequent antitumor T-cell stimulation and proliferation.