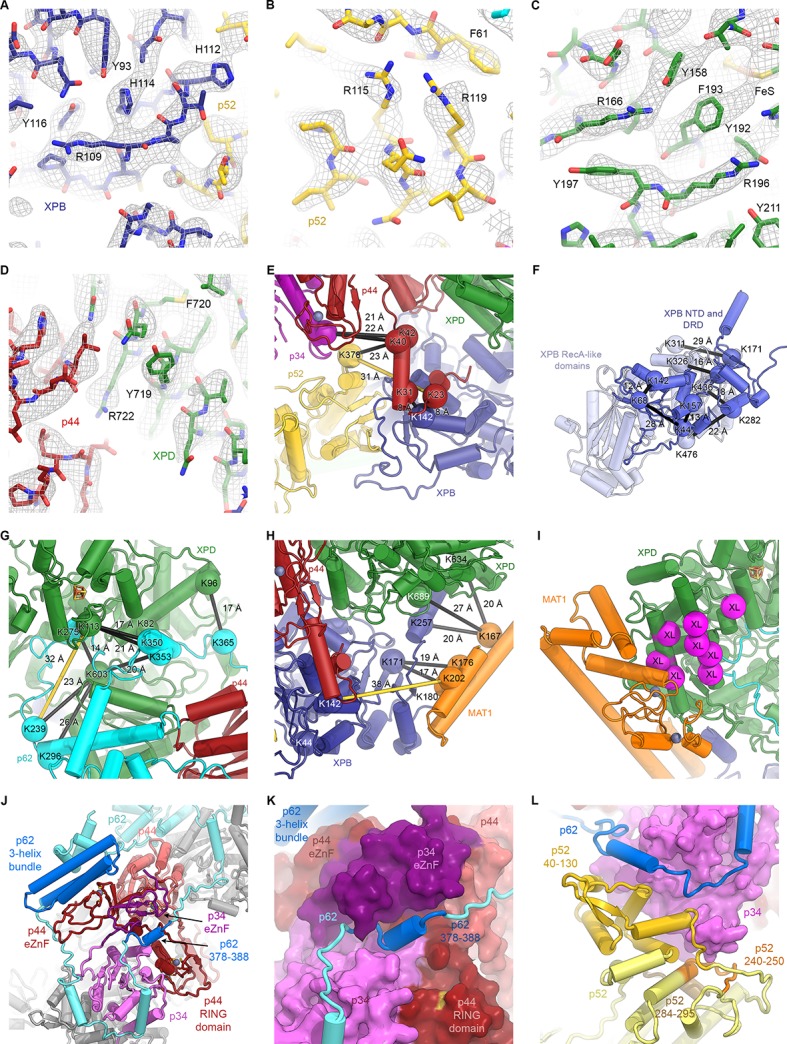
Figure 1. Structure of the TFIIH core complex.
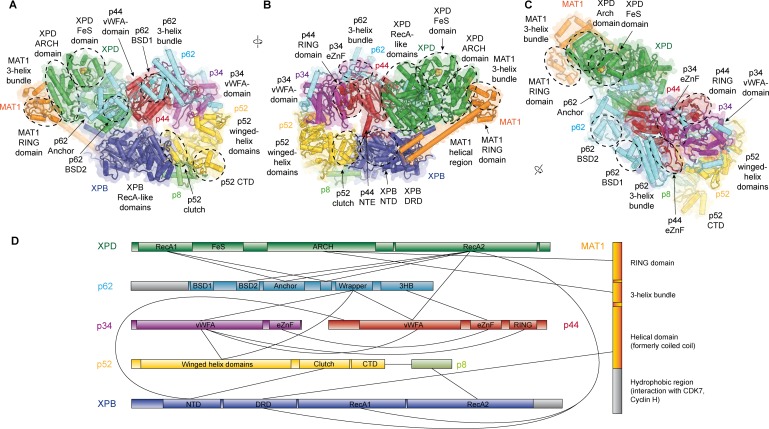
(A, B, C) Three views of the structure of the TFIIH core complex and MAT1. Subunits are color-coded and labeled (in color); individual domains are labeled (in black) and circled if needed for clarity. (D) Domain-level protein-protein interaction network between the components of the TFIIH core complex and MAT1 derived from the interactions observed in our structure. Proteins are shown with the same colors as in A and major unmodeled regions are shown in grey. Abbreviations: CTD: C-terminal domain; DRD: DNA damage recognition domain; FeS: iron sulfur cluster domain; NTD: N-terminal domain; vWFA: von Willebrand Factor A.
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Sample micrograph, sample 2D classes, and data processing scheme for global reconstruction.
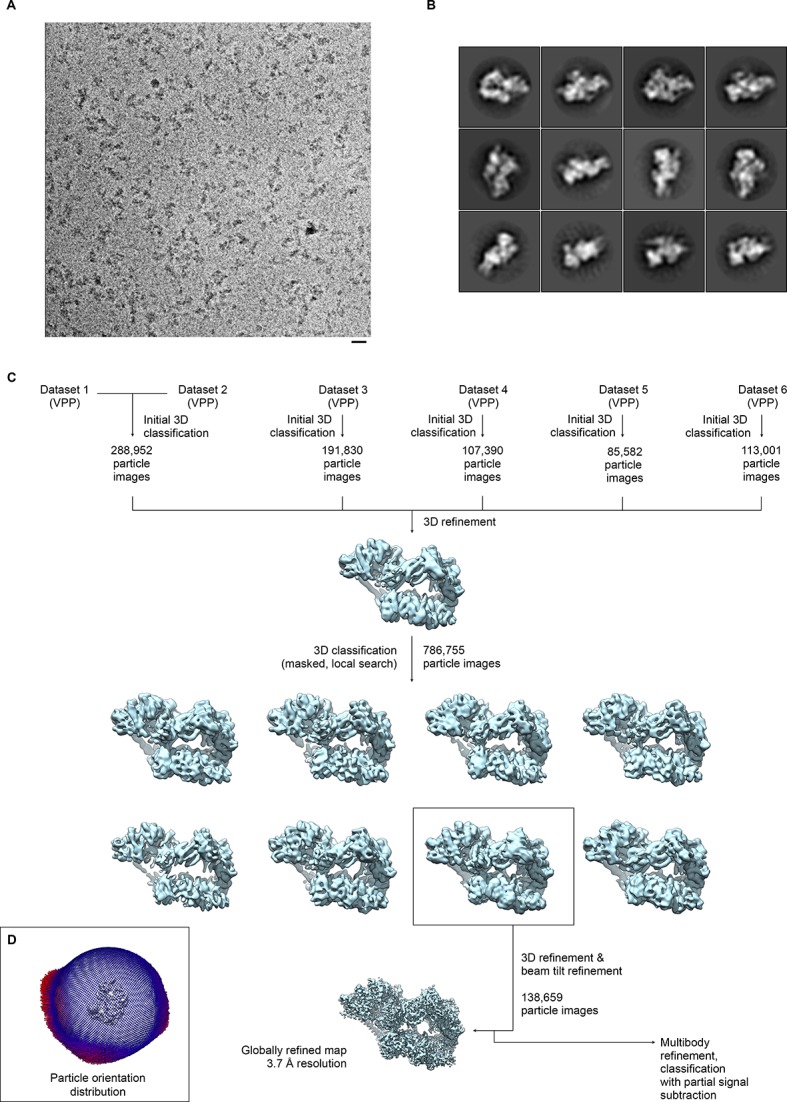
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Resolution estimation, validation statistics, and quality of the density.
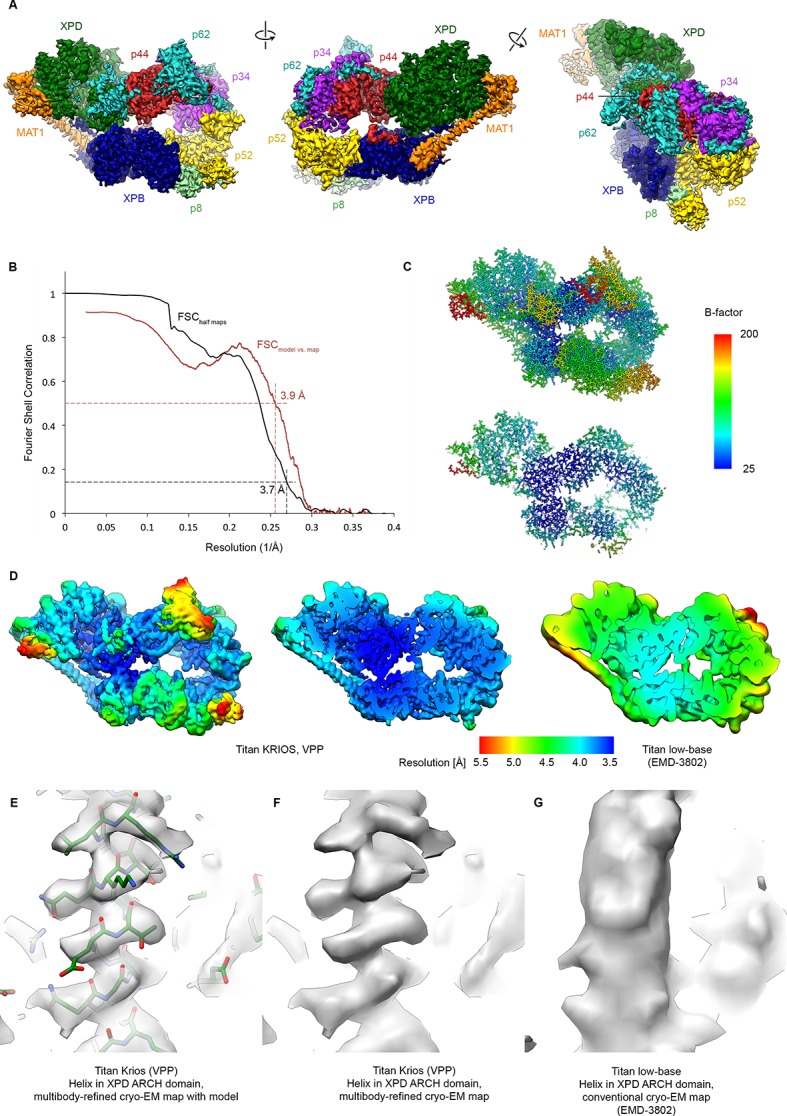
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Focused classification of the p62 BSD2 domain.
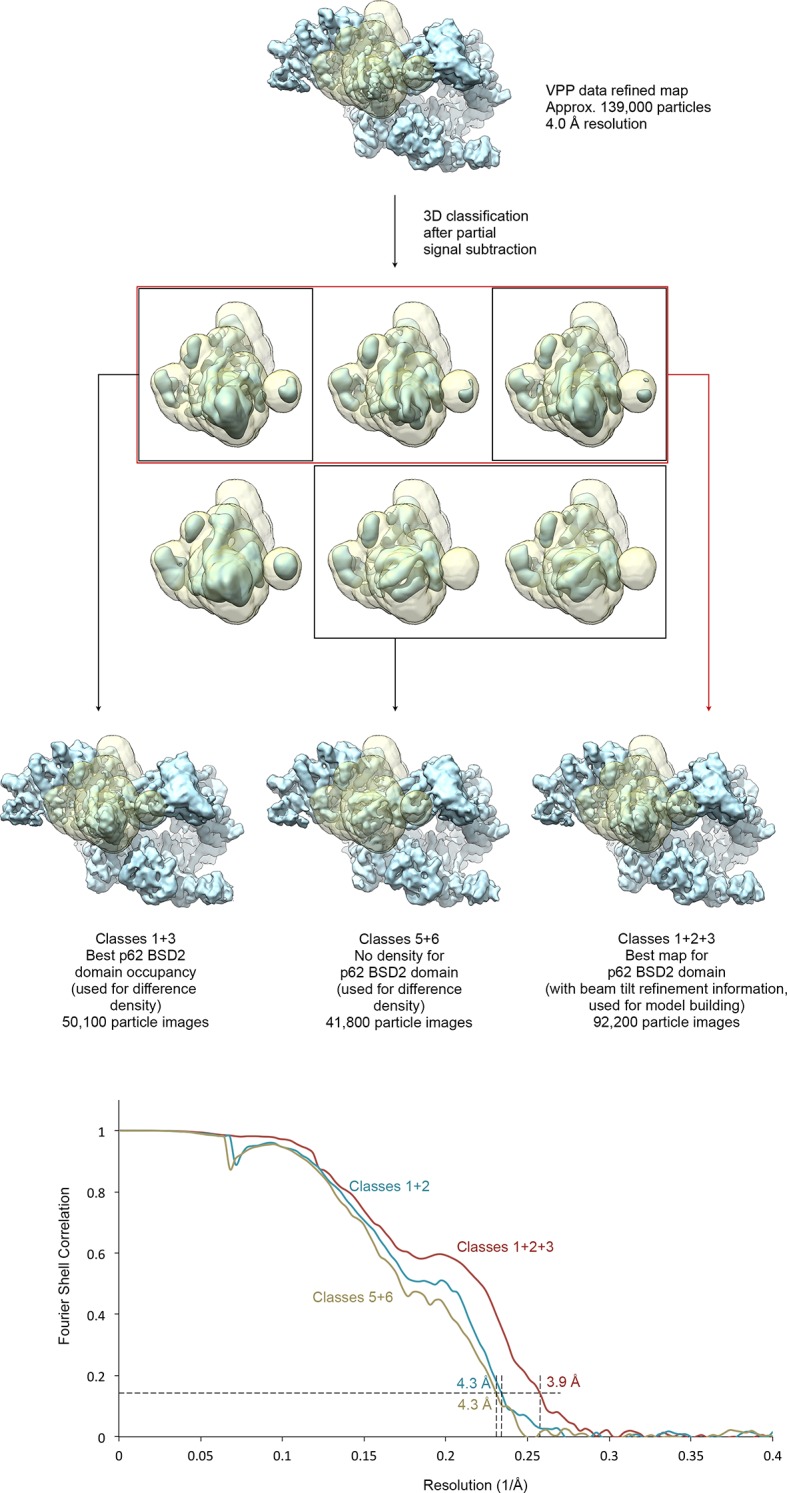
Figure 1—figure supplement 4. Focused classification and interpretation of the MAT1 RING domain density.
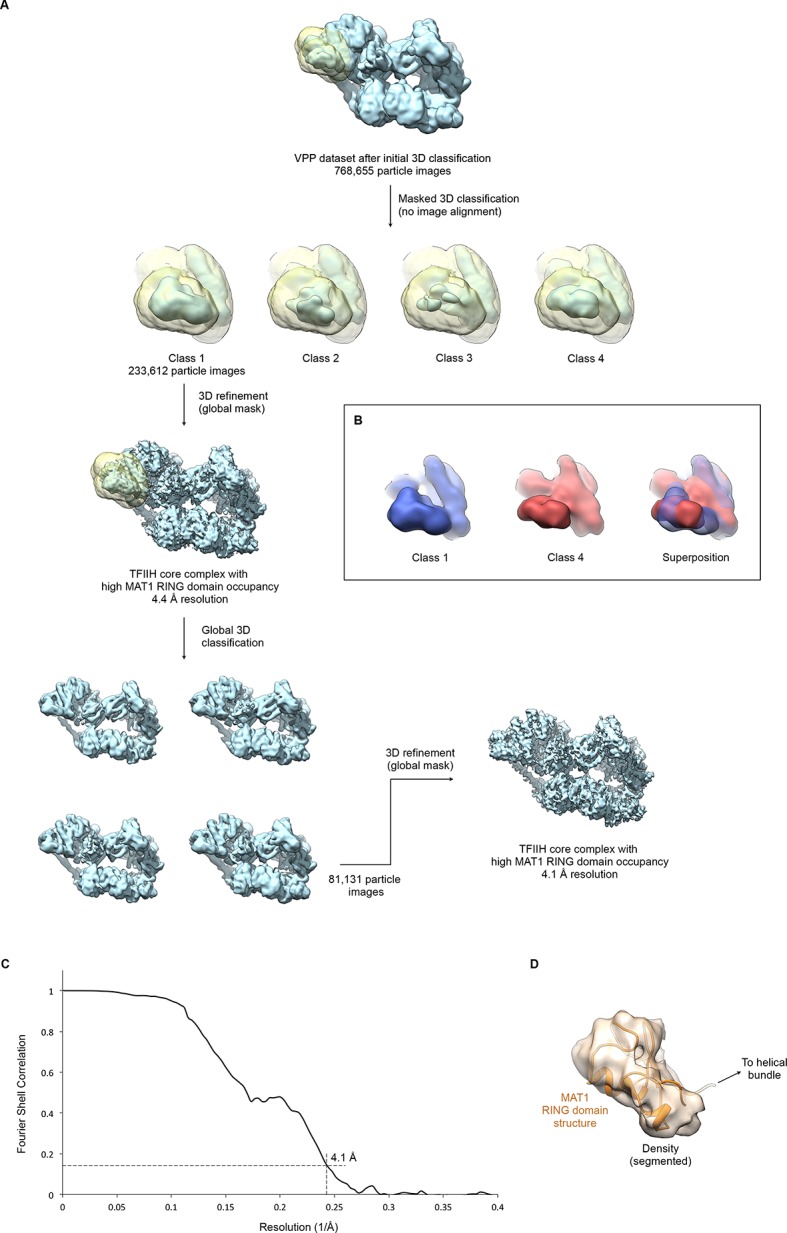
Figure 1—figure supplement 5. Multibody refinement.
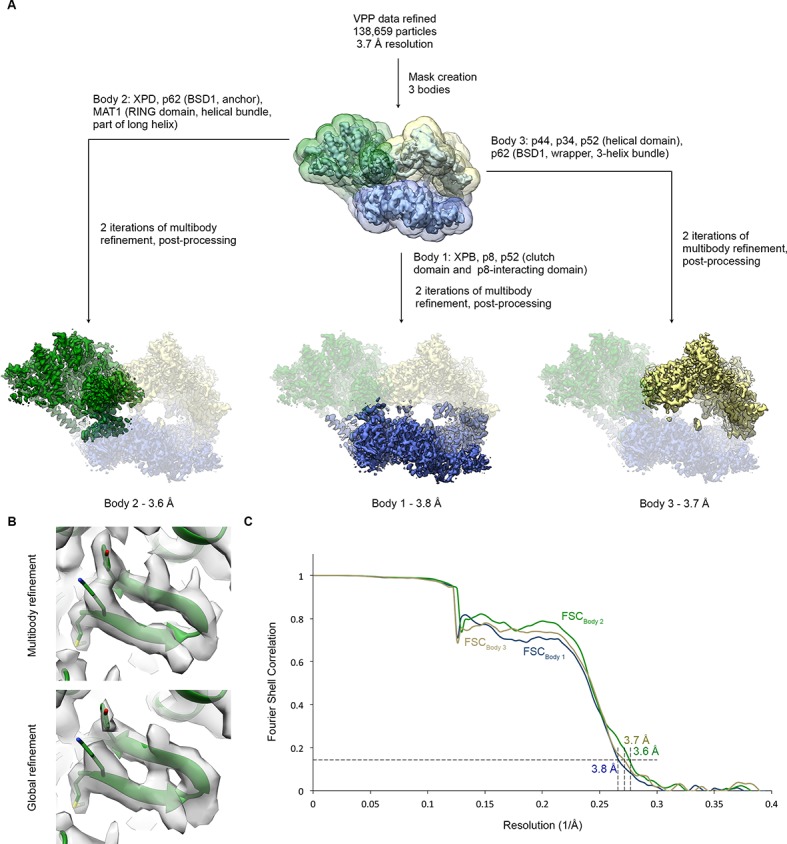
Figure 1—figure supplement 6. Detailed architecture of the TFIIH core complex.