Figure 1.
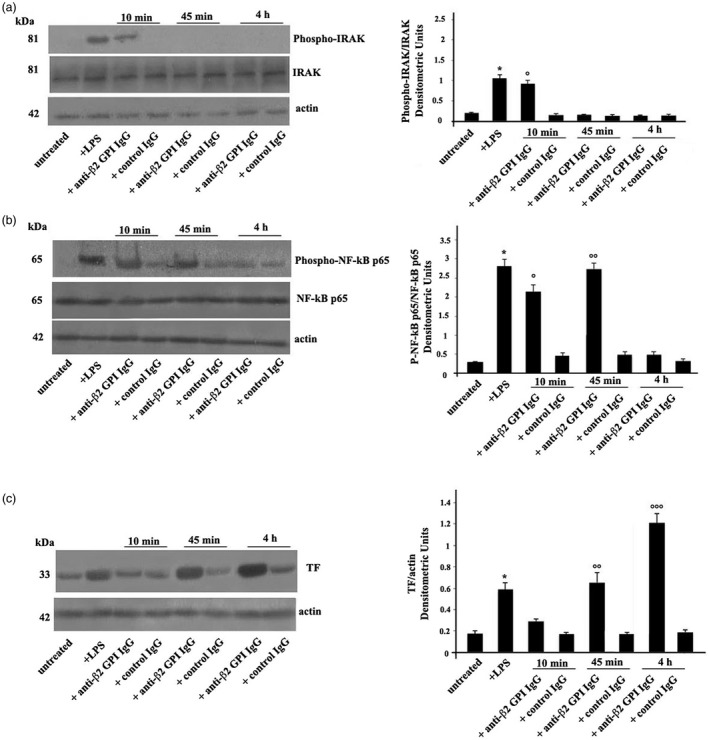
(a) Anti‐β2‐glycoprotein I (GPI) antibodies induce interleukin receptor‐associated kinase (IRAK) phosphorylation. Human platelets from healthy donors, untreated or treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 ng/ml), with control human serum immunoglobulin IgG (200 μg/ml), or with human affinity‐purified anti‐β2‐GPI IgG (200 μg/ml) for 10 min, 45 min and 4 h at 37°C, were analyzed by Western blotting using rabbit anti‐phospho‐IRAK. The membrane was stripped and reprobed with polyclonal anti‐IRAK antibody. Loading control was evaluated using anti‐actin monoclonal antibody (mAb). Right panel, densitometric phospho‐IRAK/IRAK ratios are shown. Results represent the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) from three independent experiments. *P + LPS <0·001 versus untreated, °P + anti‐β2‐GPI IgG (10 min) <0·001 versus untreated. (b) Anti‐β2‐GPI antibodies induce nuclear factor kappaB (NF‐κB) activation. Human platelets, untreated or treated with LPS, with control human serum IgG, or with human affinity‐purified anti‐β2‐GPI IgG for 10 min, 45 min and 4 h, were analyzed by rabbit anti‐phospho‐NF‐κB p65. Loading control was evaluated using anti‐actin mAb. Right panel, densitometric phospho‐NF‐κB p65/NF‐κB p65 ratios are shown. Results represent the mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. *P + LPS <0·001 versus untreated, °P + anti‐β2‐GPI IgG (10 min) <0·001 versus untreated. °°P + anti‐β2‐GPI IgG (45 min) <0·001 versus untreated. (c) Anti‐β2‐GPI antibodies induce tissue factor (TF) expression. Human platelets, untreated or treated with LPS, with control IgG, or with anti‐β2‐GPI IgG for 10 min, 45 min and 4 h, were analyzed by anti‐TF mAb. Loading control was evaluated using anti‐actin mAb. Densitometric analysis on the right panel. Results represent the mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. *P + LPS <0·001 versus untreated, °°P + anti‐β2‐GPI IgG (45 min) <0·001 versus untreated. °°°P + anti‐β2‐GPI IgG (4 h) <0·001 versus untreated.
