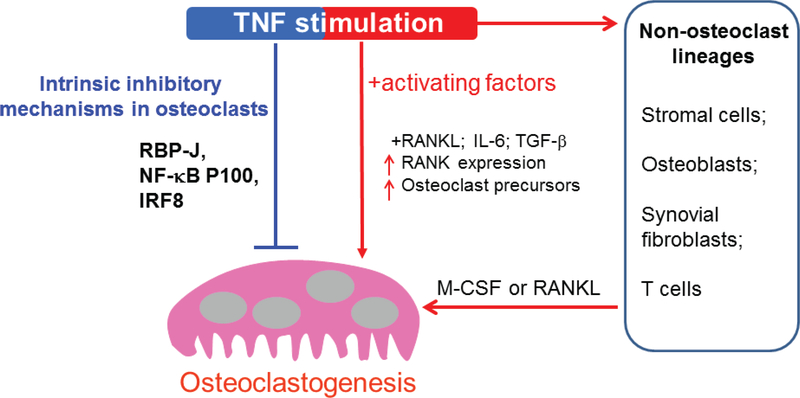
FIG. 1:
Model showing a dual role of TNF in osteoclastogenesis. TNF can stimulate proliferation of osteoclast precursors, increase RANK expression, and in most conditions act together with other cytokines and growth factors such as RANKL, IL-6, and TGF-β to synergistically promote osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vivo. TNF also indirectly promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting other cell populations such as osteoblastic/stromal cells, synovial cells, and T-cells by stimulating M-CSF or RANKL production from these cells. Recent studies have highlighted several lines of evidence showing that TNF restrains osteoclastogenesis through intrinsic feedback mechanisms such as via RBP-J, NF-[kappa]B p100/TRAF3, or IRF-8.