Figure 4.
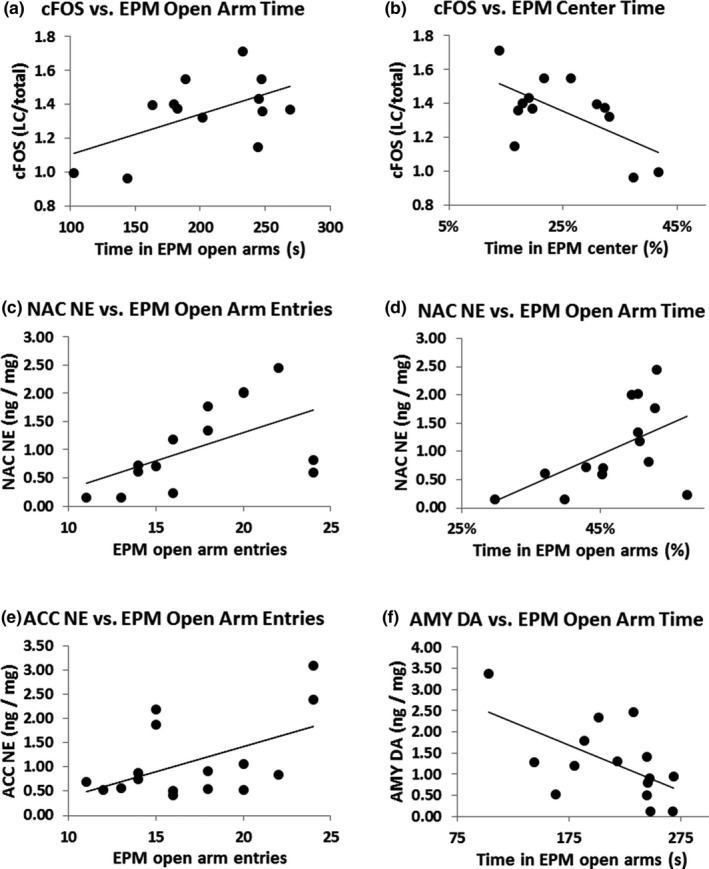
Significant correlations between neurobiological and behavioral variables. Expression of c‐fos mRNA in the locus coeruleus (LC) was positively correlated with time spent in the open arms of the elevated plus maze (EPM) (r = 0.635, p = 0.020; a). Expression of c‐fos mRNA was negatively correlated with time spent in the center of the EPM (r = −0.623, p = 0.023; b). Norepinephrine (NE) in the nucleus accumbens (NAC) was positively associated with increased open arm entries of the EPM (r = 0.540, p = 0.046; c). NE in the NAC was also positively correlated with increased percentage of time spent in the open arms of the EPM (r = 0.539, p = 0.048; d). NE in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) was positively associated with EPM open arm entries (r = 0.522, p = 0.038; e). Dopamine (DA) in the amygdala (AMY) was negatively associated with time spent in the open arms (r = −0.549, p = 0.034; f). Error bars indicate SEM
