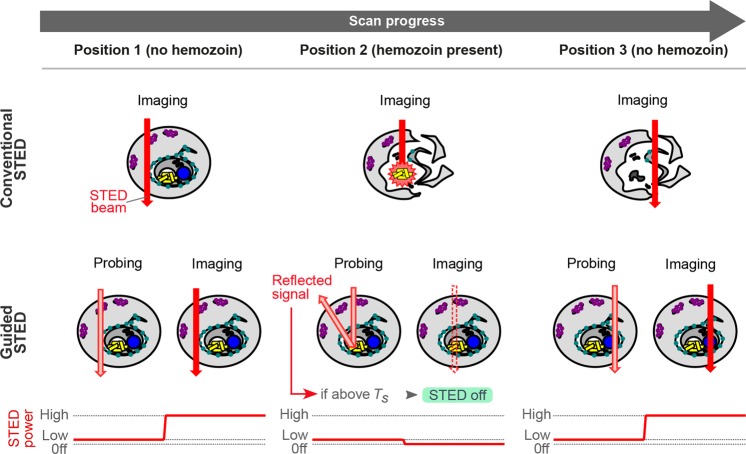
Figure 2.
Principle of guided STED for malaria samples. In conventional STED super-resolution microscopy (top row), the infected red blood cell is scanned with the STED laser (red arrow) at full power in every pixel leading to disintegration of hemozoin particles (yellow) and sample destruction. Guided STED (bottom row) can test for the presence of hemozoin at every pixel using light reflected by hemozoin particles (probing). To avoid sample damage during the probing step, the depletion laser is running at a very low power (pink). Only where the reflected light signal is below the threshold TS, the depletion laser is switched back to high power (red arrow) for super-resolution imaging.