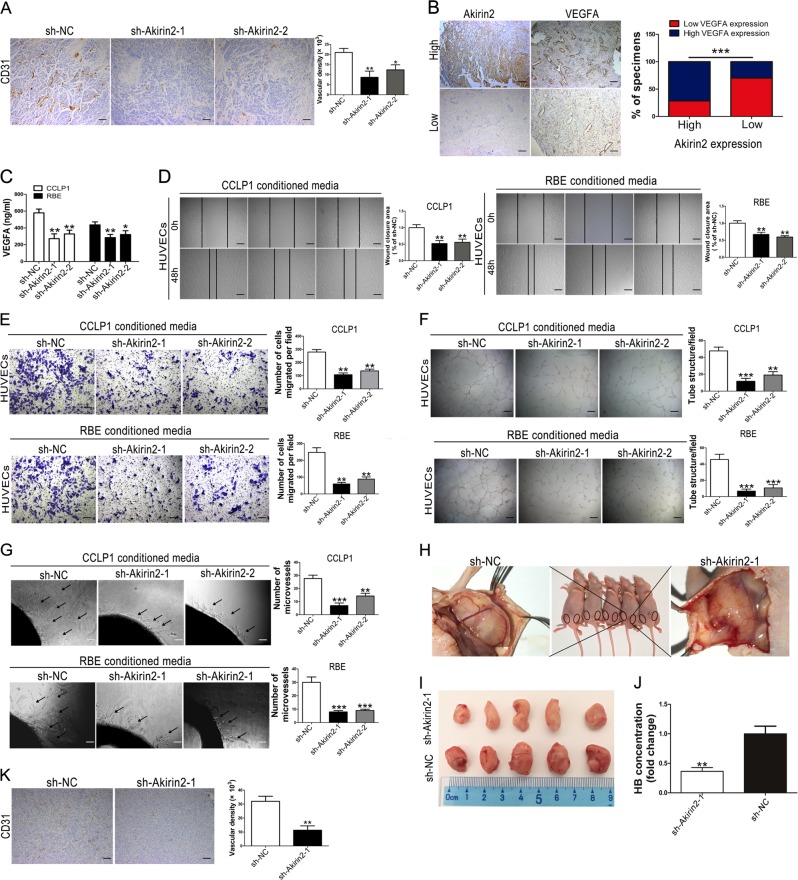
Fig. 4. Akirin2 suppression attenuates tumor angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
a CCLP1-sh-NC and CCLP1-sh-Akirin2-1 tumors were analyzed histologically using CD31-staining and CD31-staining vasculature was quantified via manually calculated average number of microvessels at × 200 magnification. b Expression of Akirin2 is associated with VEGFA expression levels in clinical cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) specimens. Two representative images are shown. The histogram displayed percentage of specimens showing low or high Akirin2 expression in relation to the expression levels of VEGFA. c The levels of VEGFA in Akirin2-sh-NC and Akirin2-sh-Akirin2 cell supernatants were detected by ELISA assay. d, e Akirin2 knockdown impaired tumor-induced HUVEC migration according to wound-healing (d) and Transwell migration assays (e). f, g Akirin2 knockdown suppressed tumor-induced HUVECs angiogenesis according to tube formation assays (f) and aortic ring sprouting assay (g). h–k Nude mice were injected on both sides of the groin subcutaneously with Matrigel mixed with the stable transfected CCLP1 cells (NC on the right side; sh-Akirin2-1 on the left side) (h). General morphology and color of the Matrigel plugs were recorded (i) and plugs were quantified for hemoglobin content (j). Vascular endothelial-like structures were examined by a CD31 staining (k). Magnification, × 40 (a, b, d, f, k), × 100 (g), × 200 (e). Scale bar, 500 μm (a, b, d, f, k), 200 μm (g), 100 μm (e). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.001. Data are shown as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments