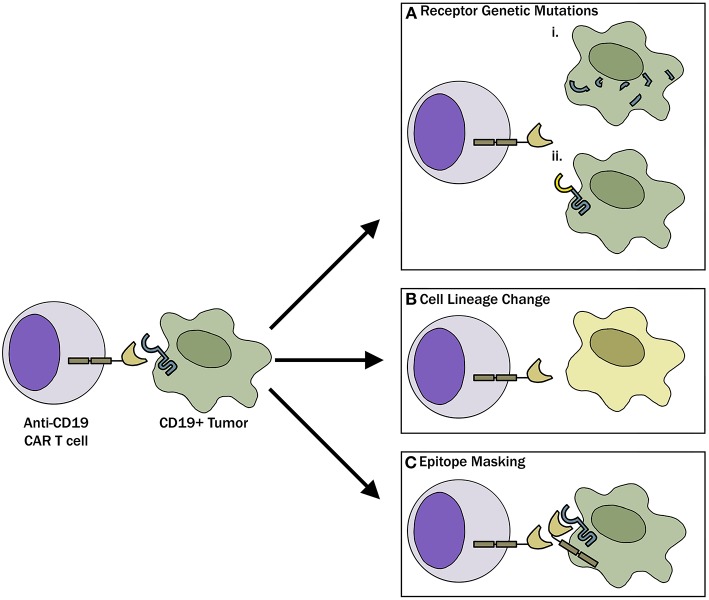
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of CAR-T evasion. (A) Tumor cells, through genetic mutations, can either (i) completely lose CD19 receptor expression or (ii) modify the CD19 receptor such that CAR-T cells can no longer recognize and bind the target. (B) Tumor cells can undergo phenotypic switch to a different lineage that is inherently CD19 negative to evade CAR-T cells. (C) As described in the case report by Ruella et al. (18) lentiviral modification of a single leukemic cell allowed for epitope masking and evasion of CAR-T cell therapy.