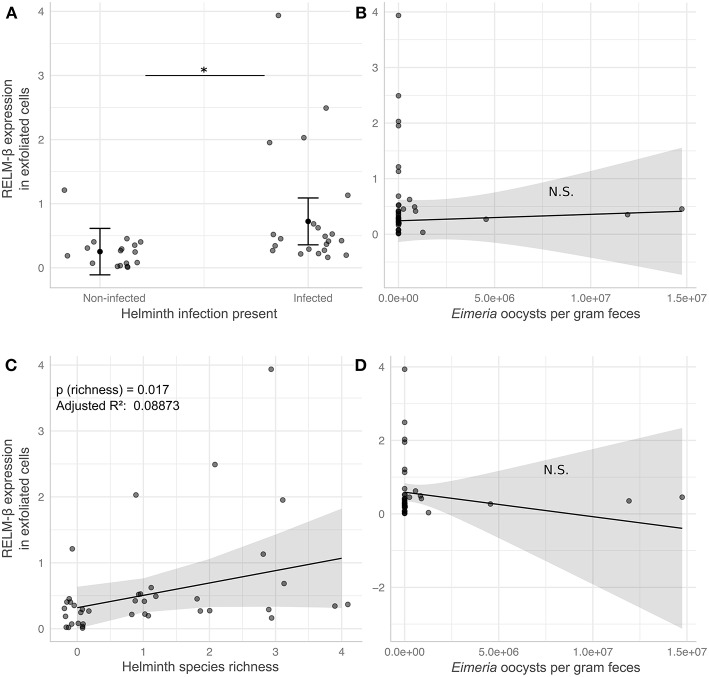
Figure 4.
RELM-β expression in exfoliated cells differs in response to helminth infection in wild house mice. Helminth and Eimeria infections were assessed in wild house mice. Linear models predict RELM-β expression to be significantly elevated by either presence (A) or species richness (C) of helminths, while the number of Eimeria oocysts shed per gram feces in the same mice has no significant effect in the respective models for presence (B) and richness (D). Gray points depict values for individual mice and are jittered relative to the x-axis to avoid overplotting in (A), solid black points and lines indicate marginal means estimated in statistical models (see Supplementary Table 4; Model 3 and Model 6), error bars and shaded areas represent 95% confidence intervals for these estimates. *P ≤ 0.05.