Figure 3.
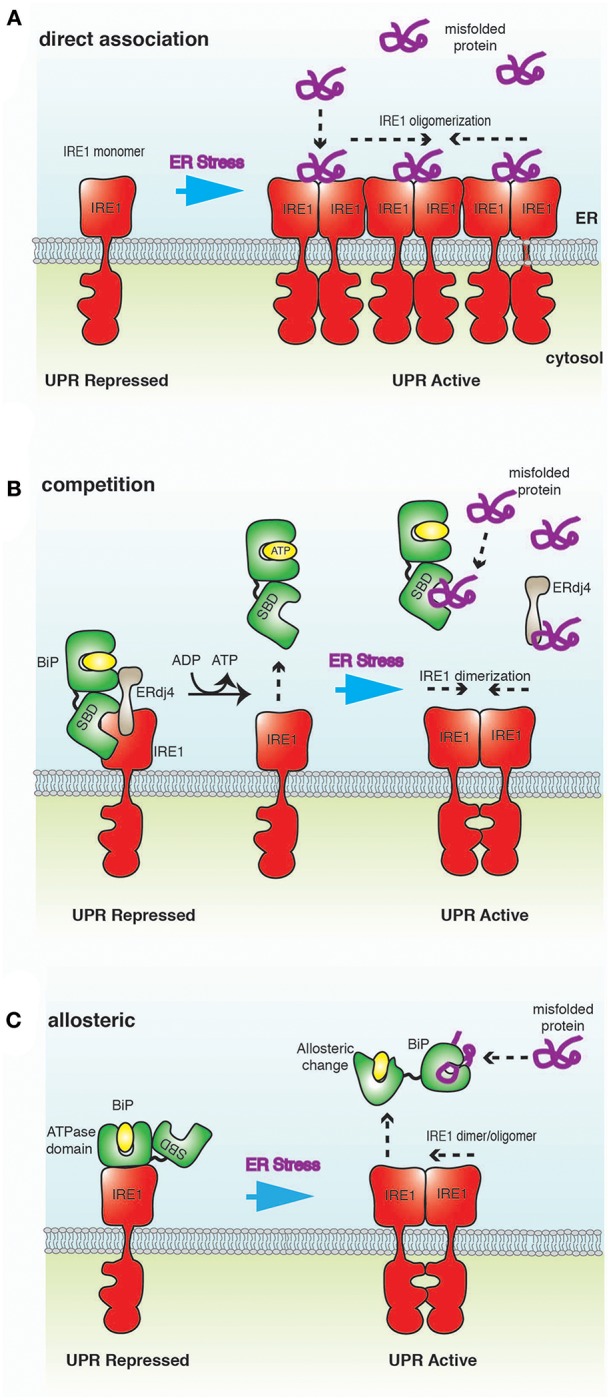
A schematic representation of ER stress-sensing mechanisms. (A) Direct association model posits that misfolded proteins bind directly to IRE1 LD, resulting in oligomerization of IRE1 and activation of UPR. (B) In the competition model, IRE1 LD binds to BiP SBD in a chaperone-substrate type interaction. This is the same site that misfolded proteins bind to BiP, leading to a competition for this binding site. BiP interaction to IRE1 is mediated by ERdj4, which ultimately inhibits UPR signaling by facilitating the formation of IRE1 LD monomer. Thus, BiP acts as a repressor of UPR signaling, but is not a direct sensor of ER stress. (C) In the allosteric model, the binding of misfolded proteins and IRE1 LD to BiP occur on different domains; thus, obviating the requirement for competition. Misfolded protein binding induces a conformational change that releases BiP from IRE1, implicating BiP as a direct sensor of ER stress.
