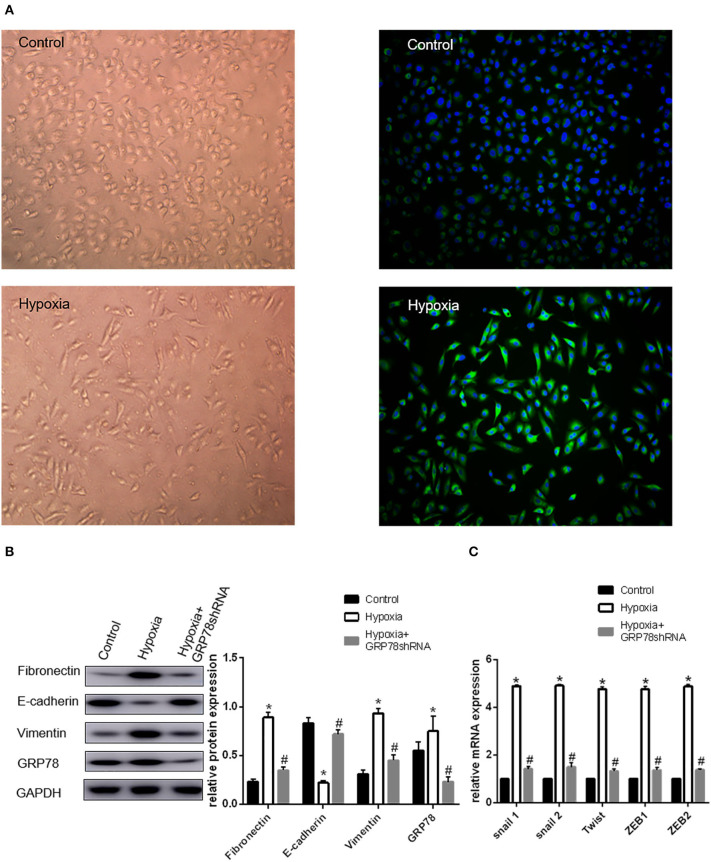
Figure 1.
Up-regulation of GRP78 plays an important role in hypoxia-induced EMT in A549 cells. (A) A549 cells acquire spindle-shaped mesenchymal morphology after 72 h of 2% O2 hypoxia (left, 100 ×). GRP78 (green fluorescence) is highly expressed in A549 cells with spindle-shaped mesenchymal morphology (right, 100 ×). (B) EMT-related markers (E-cadherin, Vimentin and Fibronectin) and GRP78 were examined by Western blot analysis (left). GAPDH was used as internal control. The protein relative value (GAPDH) is plotted in the right panel (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). *P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells under the condition of normal oxygen, the expression of E-cadherin decreases, while those of Vimentin and Fibronectin increase in A549 cells under hypoxia (2% O2 72 h). The expression of GRP78 also increases in A549 cells under hypoxia. #P < 0.05, compared with the A549 cells under the condition of hypoxia; the expression of E-cadherin increases, and those of Vimentin and Fibronectin decrease in GRP78 knockdown A549 cells under hypoxia. (C) EMT-related genes including Snail1, Snail2, Twist, ZEB1, and ZEB2 were examined by real-time quantitative PCR; mRNA expression relative value (control group) is plotted (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). *P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells in the control group, the mRNA expression levels of EMT-related genes including Snail1, Snail2, Twist, ZEB1, and ZEB2 increase under hypoxic condition (2% O2 72 h); #P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells under the condition of hypoxia, the mRNA expression levels of EMT-related genes decrease in GRP78 knockdown A549 cells under hypoxia.