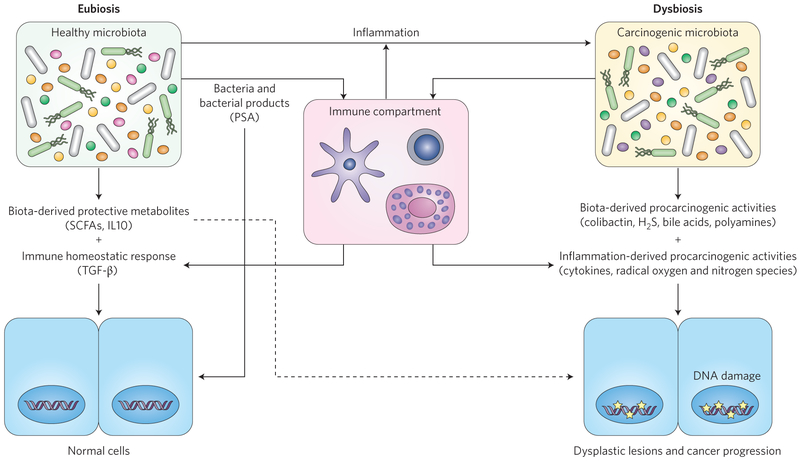
Figure 2 ∣. Microbial interactions with the immune system modulate cancer risk.
Microbiota promote homeostasis directly through metabolites and bacterial products, which influence both the epithelial and immune cell response. In addition, dysregulated immune-host interaction favours the development of dysbiosis, which contributes to carcinogenesis through metabolic activities and activation of immune responses. Some protective microbiota (SCFAs) may promote cellular proliferation of cancer-initiated cells (dashed arrow). Brackets contain example compounds. PSA, polysaccharide A; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β. Stars indicate DNA damage.