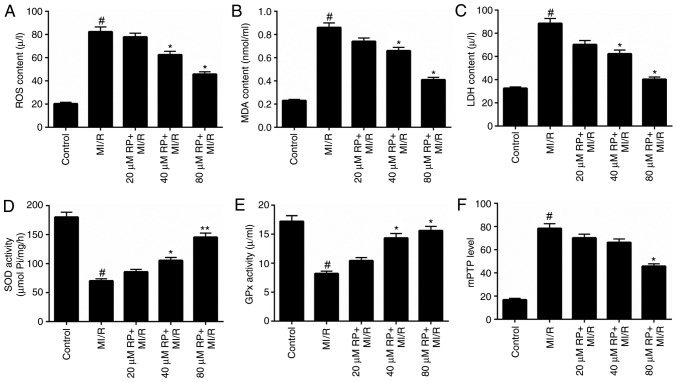
Figure 2.
RP decreases the oxidative stress and mPTP level of MI/R-induced cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes were treated with MI/R, 20 µM RP+MI/R, 40 µM RP+MI/R and 80 µM RP+MI/R. (A) ROS levels were detected by flow cytometric analysis. (B) MDA content, (C) LDH activity, (D) SOD activity and (E) GPx activity in cardiomyocytes were measured using commercial kits. (F) Spectrophotometry was performed to detect the degree of mPTP openness in cardiomyocytes. #P<0.05 vs. Control; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. MI/R. RP, rhynchophylline; mPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA, malondialdehyde; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; MI/R, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.