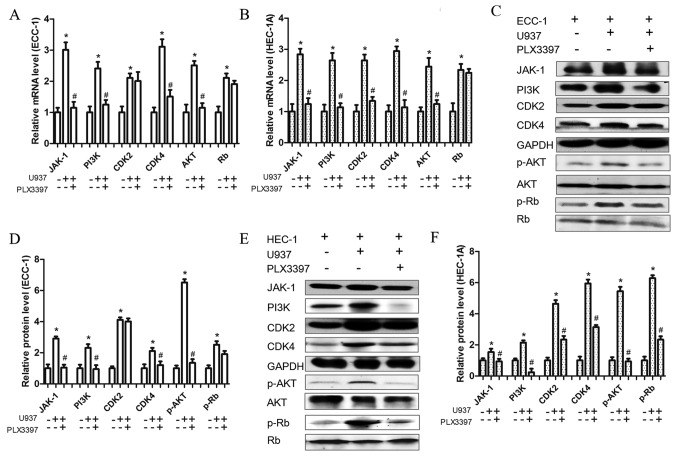
Figure 5.
CSF-1R inhibitor influences proliferation-associated protein expression. (A and B) mRNA expression levels of JAK-1, PI3K, AKT, CDK2, CDK4 and Rb, in (A) ECC-1 and (B) HEC-1A cells and their inhibition by the CSF-1R inhibitor PLX3397 (10 µM), as measured by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. (C) Protein expression of JAK-1, PI3K, p-AKT, CDK2, CDK4 and p-Rb and (D) relative quantification of their expression levels in ECC-1 cells and their inhibition by the CSF-1R inhibitor PLX3397 (10 µM), as measured by western blotting. (E) Protein expression of JAK-1, PI3K, p-AKT, CDK2, CDK4 and p-Rb and (F) relative quantification of their expression levels in HEC-1A cells and their inhibition by the CSF-1R inhibitor PLX3397 (10 µM), as measured by western blotting. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from 5 independent experiments; *P<0.05 vs. Control; #P<0.05 vs. U937 cells and ECC-1 or HEC-1A cells co-culture group. CDK4, cyclin-dependent kinase 4; CSF, colony-stimulating factor; CSF-1R, colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor; EC, endometrial cancer; JAK, Janus kinase; p, phosphorylated; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Rb, retinoblastoma-associated protein.