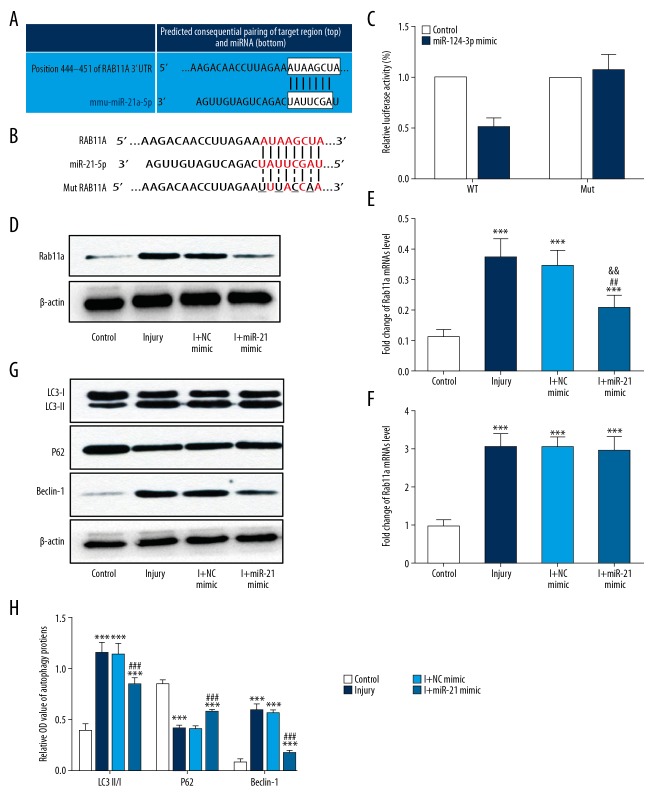
Figure 5.
miR-21-5p targeted Rab11a via repressing translation in HT-22 neurons. (A) The potential binding sites for miR-21-5p in the Rab11a 3′UTR, which were predicted by using bioinformatics analysis (http://www.targetscan.org/). (B) The WT (Rab11a WT 3′UTR) and mutant type (Rab11a mut 3′UTR) luciferase reporter constructs exhibited intact and mutated seed sequences (underlined), respectively, in the miR-21-5p binding site. (C) The relative luciferase activity of the WT and mut reporter constructs, which were co-transfected with either the miR-21–5p mimic or scrambled oligonucleotides. Data indicated that miR-21-5p inhibited the luciferase activity of the WT, but not the mut type. (D, E) Immunoblot analysis showed that Rab11a expression was upregulated in the cultured HT22 neurons after scratch injury. Overexpression of miR-21-5p suppressed the protein expression of Rab11a, and no apparent difference was observed in I+ NC mimic group, relative to the levels observed in injury group. (F) No obvious differences in Rab11a mRNA expression were observed among the injury group and transfected groups. (G, H) Immunoblot analysis of autophagy-related proteins (LC3, P62, Beclin-1) showed that neuronal autophagy was inhibited in the I+miR-21-5p mimic group, and no apparent difference was observed in the I+ NC mimic group, relative to the levels observed in injury group. *** P<0.001 versus control group; ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 versus injury group. WT – wild-type; Mut – mutant-type; NC – negative control.