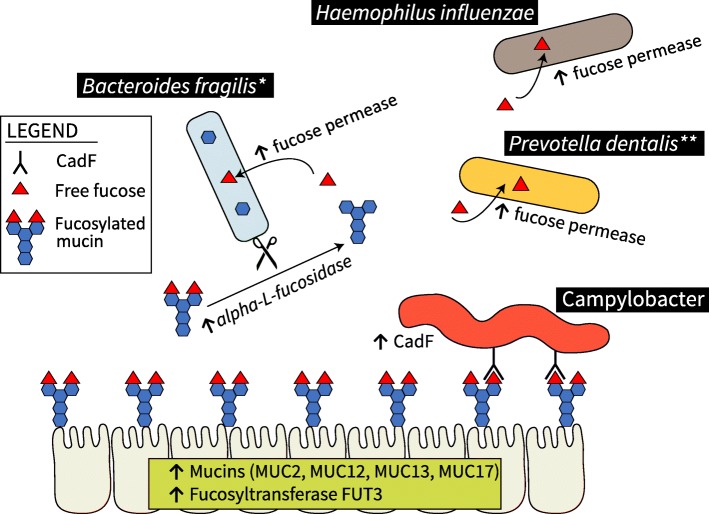
Fig. 8.
Overview of proposed mechanisms by which fucose is utilized in ICD. Fucose is depicted by red triangles; mucins are depicted by chains of blue hexagons. Host cells (bottom of figure) increase the expression of enterocyte-derived mucins and a fucosyltransferase. Bacteroides species increase the expression of alpha-l-fucosidases, which are secreted enzymes that cleave fucose from host-derived fucosylated mucins, thereby increasing the amount of free fucose in the lumen. Species like Haemophilus influenzae and Prevotella dentalis increase the expression of fucose permease which enables increased uptake of free fucose. Campylobacter does not increase the expression of fucose permease in ICD, but it does increase the expression of cadF, a protein that enables adherence to fucosylated mucins